jq研究
难度-Easy
jq研究
jq研究
jq呢是对json数据的操作,主要让数据能轻松美化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
-n, --null-input use `null` as the single input value;
-R, --raw-input read each line as string instead of JSON;
-s, --slurp read all inputs into an array and use it as
the single input value;
-c, --compact-output compact instead of pretty-printed output;
-r, --raw-output output strings without escapes and quotes;
--raw-output0 implies -r and output NUL after each output;
-j, --join-output implies -r and output without newline after
each output;
-a, --ascii-output output strings by only ASCII characters
using escape sequences;
-S, --sort-keys sort keys of each object on output;
-C, --color-output colorize JSON output;
-M, --monochrome-output disable colored output;
--tab use tabs for indentation;
--indent n use n spaces for indentation (max 7 spaces);
--unbuffered flush output stream after each output;
--stream parse the input value in streaming fashion;
--stream-errors implies --stream and report parse error as
an array;
--seq parse input/output as application/json-seq;
-f, --from-file file load filter from the file;
-L directory search modules from the directory;
--arg name value set $name to the string value;
--argjson name value set $name to the JSON value;
--slurpfile name file set $name to an array of JSON values read
from the file;
--rawfile name file set $name to string contents of file;
--args consume remaining arguments as positional
string values;
--jsonargs consume remaining arguments as positional
JSON values;
-e, --exit-status set exit status code based on the output;
-V, --version show the version;
--build-configuration show jq's build configuration;
-h, --help show the help;
-- terminates argument processing;
从简单到难的过渡,我先每一个命令操作输出一下看看效果
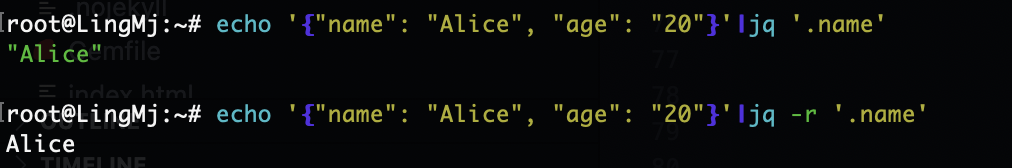
先是提取对应字段的值,效果像键值一样
1
2
3
echo '{"name": "Alice", "age": "20"}'|jq '.name'
echo '{"name": "Alice", "age": "20"}'|jq -r '.name'
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]'|jq -r '.[]| .name'
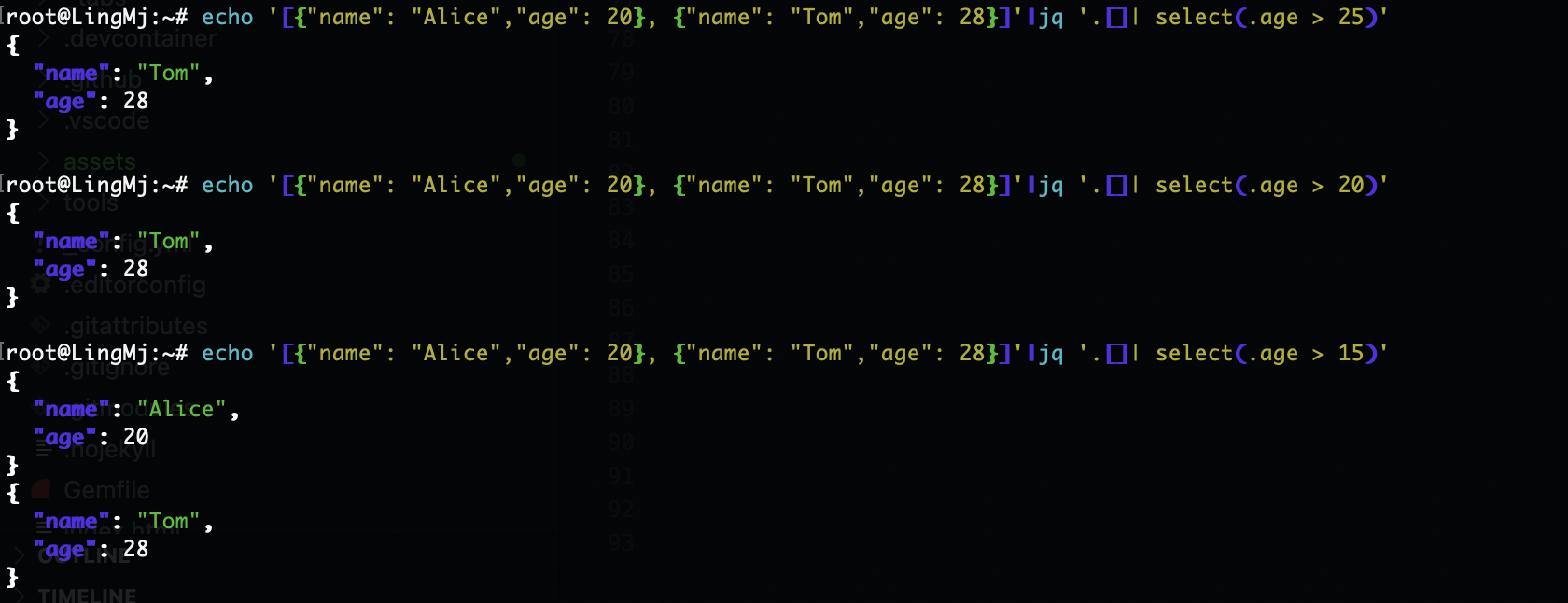
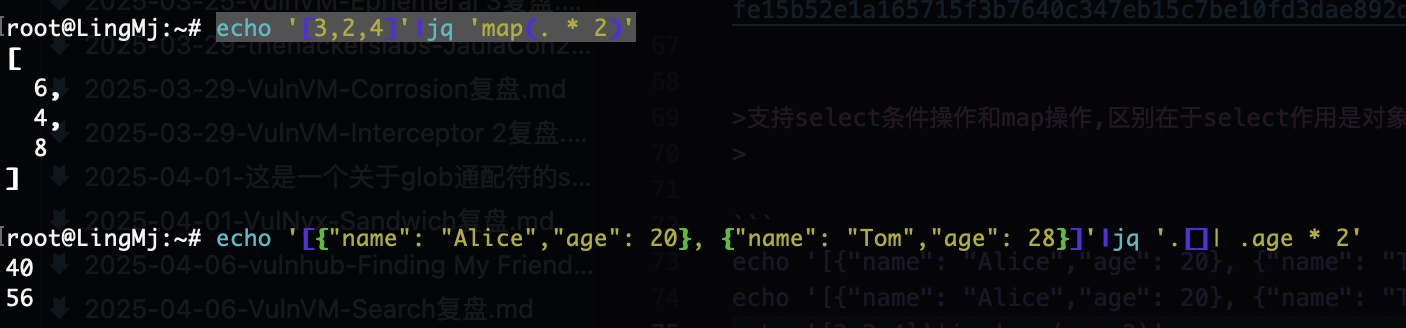
支持select条件操作和map操作,区别在于select作用是对象,map作用是元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]'|jq '.[]| select(.age > 25)'
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]'|jq '.[]| select(.age > 15)'
echo '[3,2,4]'|jq 'map(. * 2)'
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]'|jq '.[]| .age * 2'
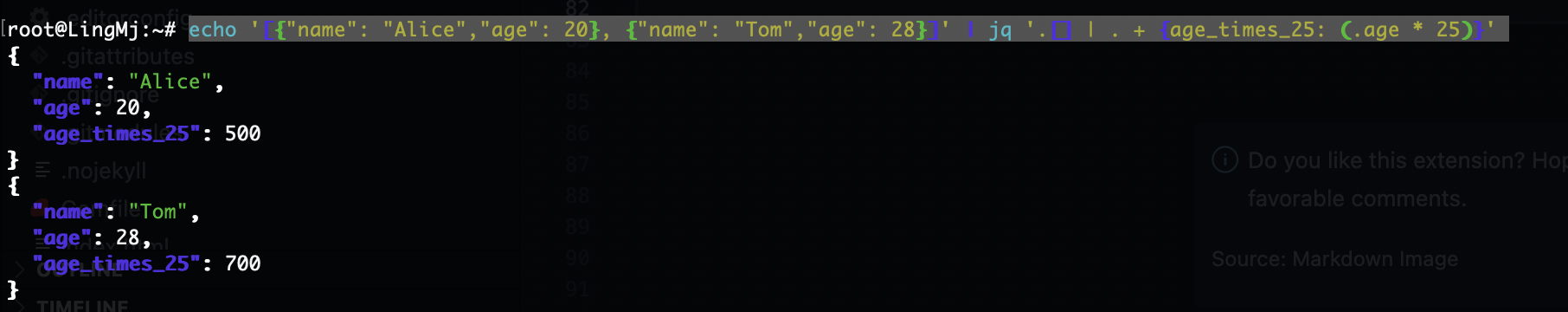
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]' | jq '.[] | . + {age_times_25: (.age * 25)}'
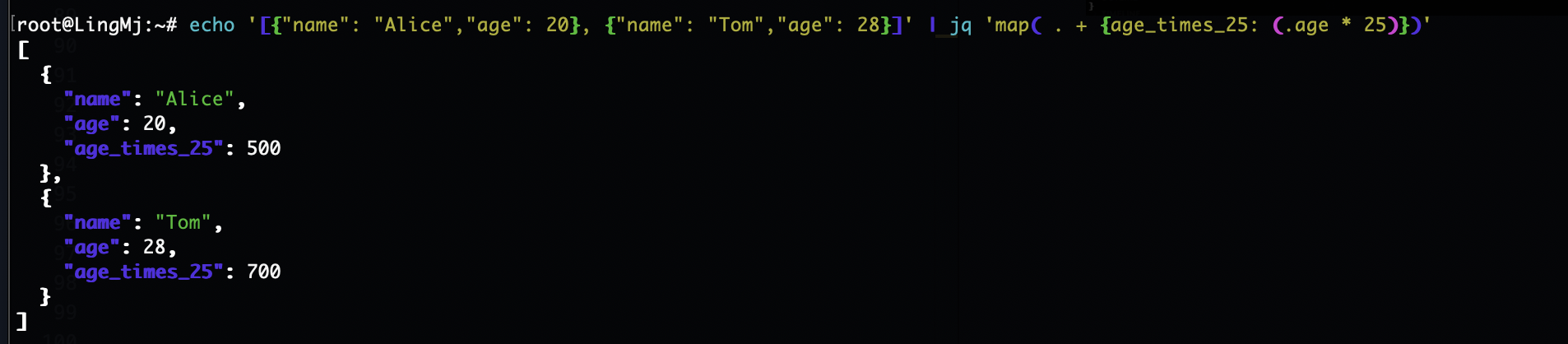
echo '[{"name": "Alice","age": 20}, {"name": "Tom","age": 28}]' | jq 'map( . + {age_times_25: (.age * 25)})'
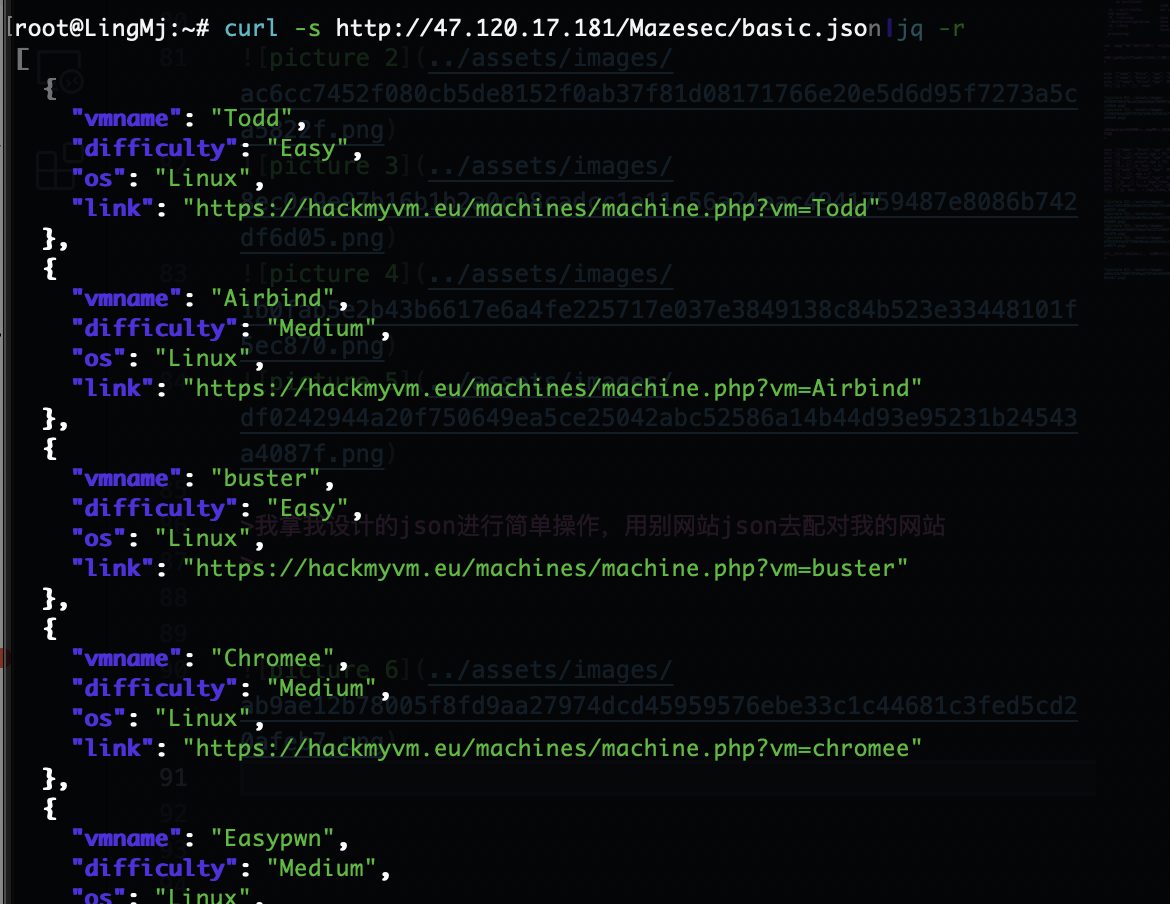
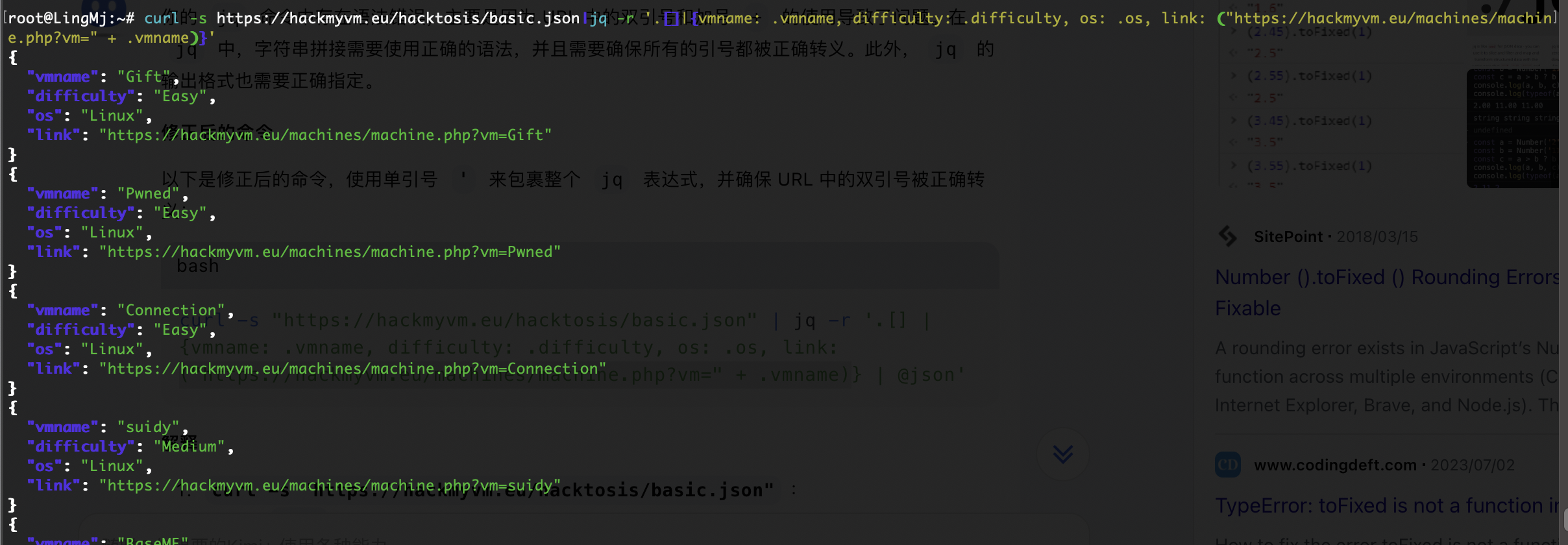
我拿我设计的json进行简单操作,用别网站json去配对我的网站
可以看到一个倒序就能完成一摸一样的效果
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.