niuke Linked list复盘
难度-Easy
第一题 BM1 反转链表
给定一个单链表的头结点pHead(该头节点是有值的,比如在下图,它的val是1),长度为n,反转该链表后,返回新链表的表头。 数据范围: 要求:空间复杂度 ,时间复杂度 。 如当输入链表{1,2,3}时, 经反转后,原链表变为{3,2,1},所以对应的输出为{3,2,1}。 以上转换过程如下图所示:示例1 输入 {1,2,3} 输出 {3,2,1} 示例2 输入{} 输出 {}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def ReverseList(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
prev = None
curr = head
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
return prev
代码解释:先定义2个变量,一个为prev上一个,一个为链表curr,链表curr存储第一个元素head,循环这个链表从左往右头端开始,当curr没有下一个为空终止循环,所以循环内部定义next_node = curr.next存储下一个节点,然后下一个节点curr.next = prev,此时从开始为空prev,进行赋值,下一次循环即可将值进行互换,prev = 等于当前节点,curr = next_node 下一个节点循环将节点往前移动
第二题 链表内指定区间反转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @param m int整型
# @param n int整型
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self , head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
#定义一个新的链表
dummpy = ListNode(0)
dummpy.next = head
prev = dummpy
for _ in range(1, m):
prev = prev.next # 这里步骤是保证我们可以设计前缀节点是开始节点得到上一个
curr = prev.next # 这样开始节点就是我们要的区间反转的第一个端值
for _ in range(n - m):
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = next_node.next
next_node.next = prev.next
prev.next = next_node
return dummpy.next
这个区间反转链表的话,先定义一个新的链表用于控制反转的,前缀用循环的方式进行移动,移动到我们开始反转链表的前一个值,需要进行反转链表的次数是区间值,反转链表没有特殊变换,区别在与区间prev.next对应反转整个连curr,区间反转链表next_node.next是反转整个链表的prev
第三题 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @param k int整型
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self , head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
temp = head
for _ in range(k):
if not temp:
return head
temp = temp.next
prev = None
curr = head
for _ in range(k):
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
head.next = self.reverseKGroup(curr, k)
return prev
这个的话和整个反转链表差不多,主要是利用递归的方式,先临时定义一个控制区间在k即可递归是下一个head是当前end的下一个
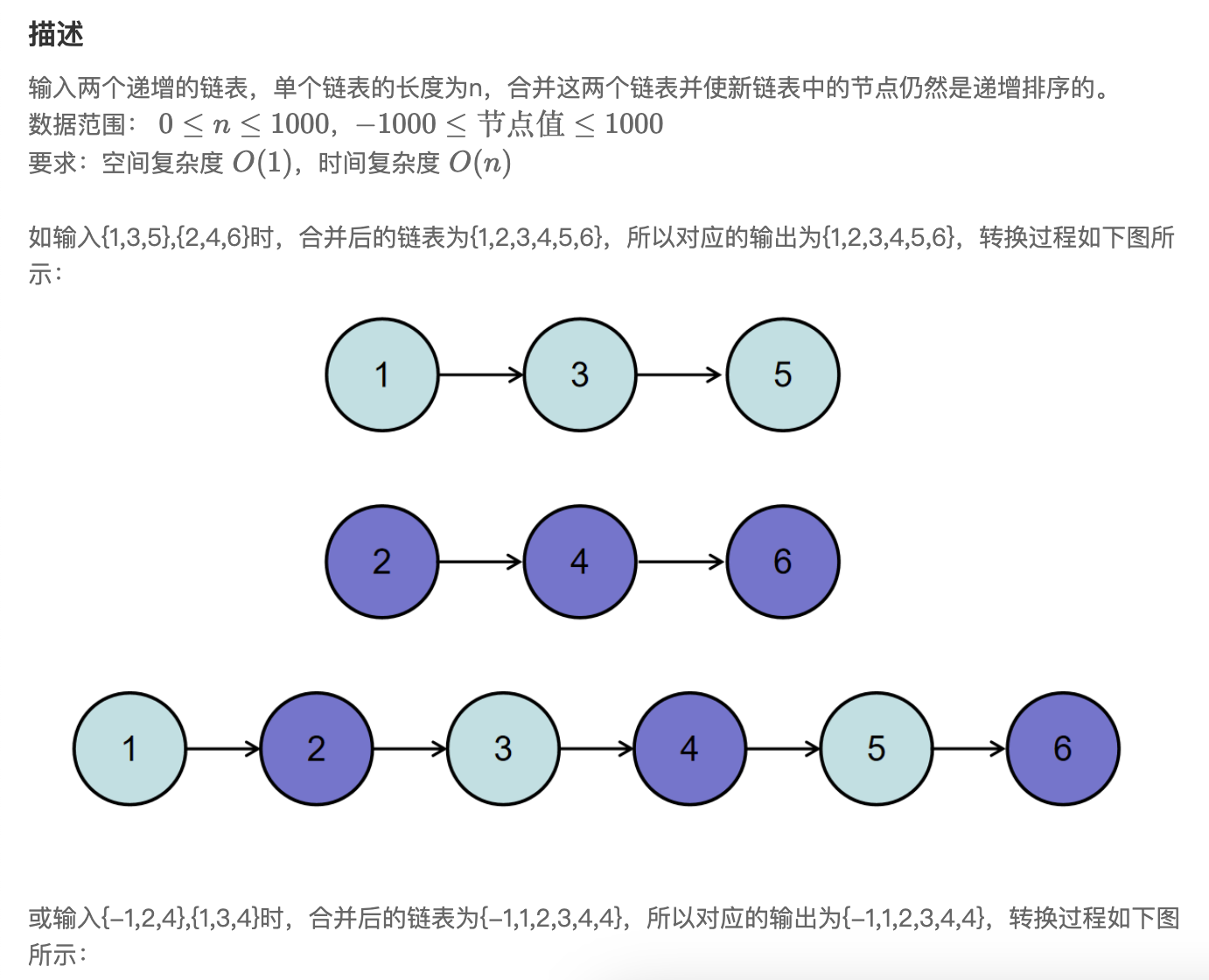
第四题 合并两个排序的链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pHead1 ListNode类
# @param pHead2 ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def Merge(self , pHead1: ListNode, pHead2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not pHead1:
return pHead2
if not pHead2:
return pHead1
if pHead1.val <= pHead2.val:
pHead1.next = self.Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
else:
pHead2.next = self.Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
这个好像leetcode写过,先判断是否存在空链表,如果存在直接返回另外一个链表的节点,然后是判断链表的下一个节点应该跟那个那个节点进行对比并返回
第五题 合并k个已排序的链表
这个明显难度比之前高,我选择2个方案解决一个是最小堆(优先队列)的方法,另一个是分治合并方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 最小堆方案
import heapq
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self , lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
# write code here
dummy = ListNode(0)
curr = dummy
heap = []
counter = 0
for node in lists:
if node:
heapq.heappush(heap, (node.val, counter, node))
counter += 1
while heap:
val, cnt, node = heapq.heappop(heap)
curr.next = node
curr = curr.next
if node.next:
heapq.heappush(heap, (node.next.val, counter, node.next))
counter += 1
return dummy.next
最小堆方案就是定义一个新的链表,从第一个链表开始不断弹出链表的最小节点加入堆直到堆为空用计数器比较节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
# 分治合并法
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param lists ListNode类一维数组
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self , lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
temp_lists = [l for l in lists if l]
if not temp_lists:
return None
if len(temp_lists) == 1:
return temp_lists[0]
lists = temp_lists
while len(lists) > 1:
new_lists = []
for i in range(0, len(lists), 2):
if i + 1 < len(lists):
merged = self.mergeTwo(lists[i], lists[i+1])
new_lists.append(merged)
else:
new_lists.append(lists[i])
lists = new_lists
return lists[0] if lists else None
def mergeTwo(self, lists1, lists2):
if not lists1 and not lists2:
return None
if not lists1:
return lists2
if not lists2:
return lists1
dummy = curr = ListNode(0)
while lists1 and lists2:
if lists1.val < lists2.val:
curr.next = lists1
lists1 = lists1.next
else:
curr.next = lists2
lists2 = lists2.next
curr = curr.next
curr.next = lists1 if lists1 else lists2
return dummy.next
这个分治合并法原理不难但是写的时候对我很难,首先原理是先定义一个函数进行链表合并这个之前写过所以没有难度部分,主要是控制整个数组分成两组进行合并,剩单个直接加入链表,这里还有定义链表为空或者数组为空的时候,创建一个不断循环的新数组进行操作
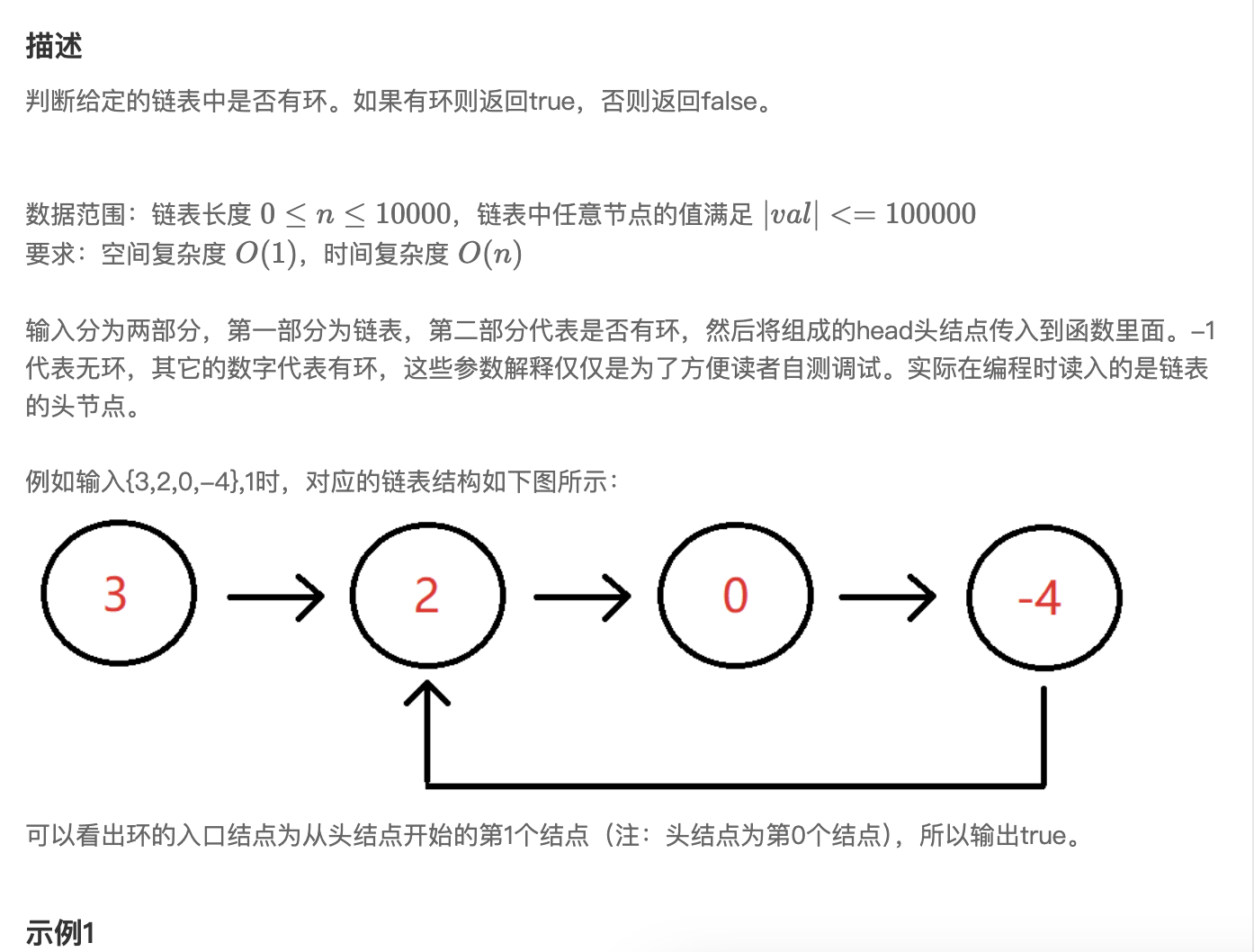
第六题 判断链表中是否有环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
from sys import float_repr_style
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self , head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head or not head.next:
return False
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
return True
return False
这个考虑的是快慢指针节点是否相同相同为true其他为false,慢指针移动1格,快指针移动2格
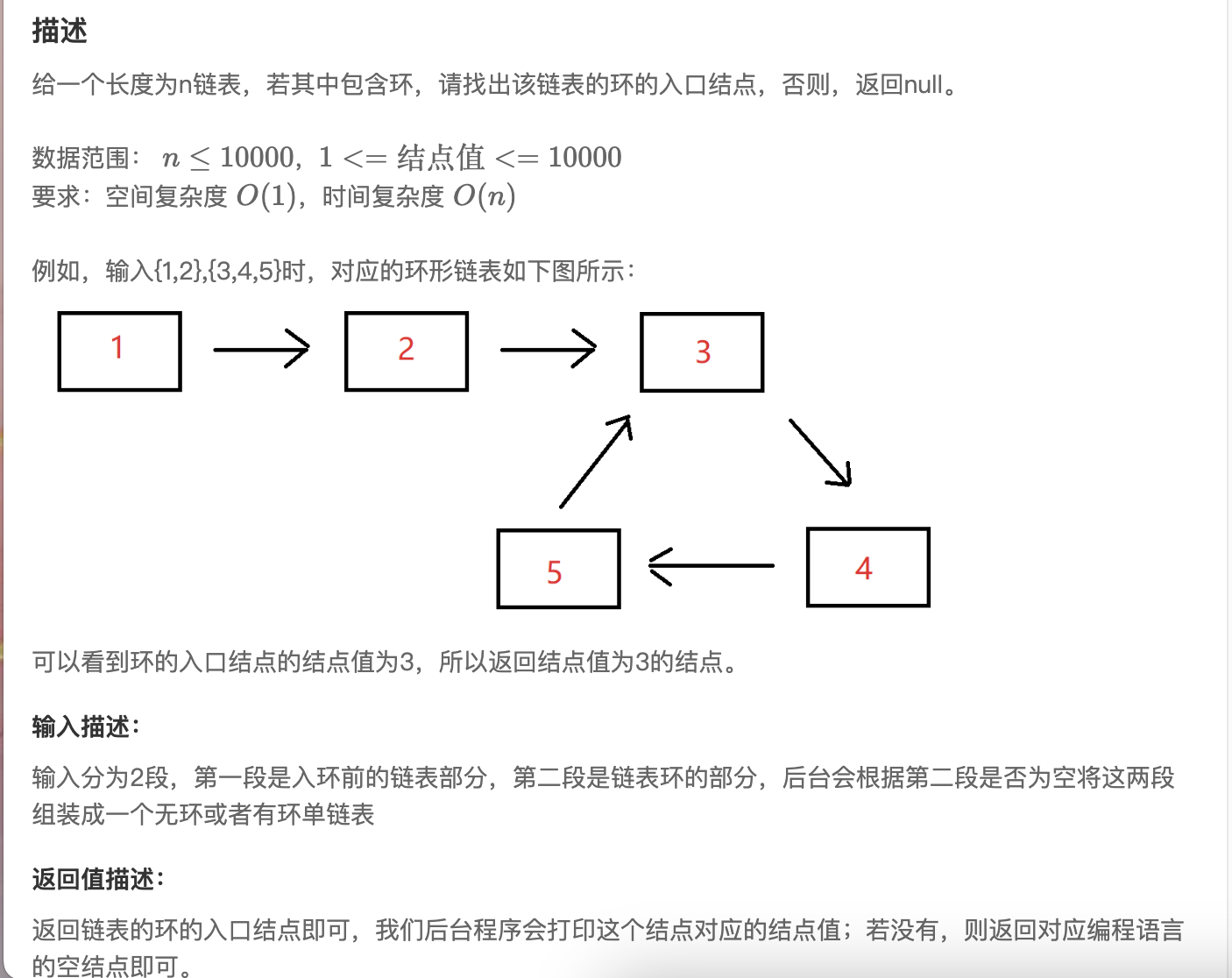
第七题 链表中环的入口结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
if not pHead or not pHead.next:
return None
fast = slow = pHead
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
break
else:
return None
slow = pHead
while slow != fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
主要是先判断是否为有环,有环情况入口就是快慢指针相遇的位置,所以当第一次相遇时break此时我们得到的节点是为尾节点,慢指针从头开始进行当再次相遇的时候就说入口,此时指针第二次都是移动一格
第八题 链表中倒数最后k个结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pHead ListNode类
# @param k int整型
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self , pHead: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if k <= 0 or not pHead:
return None
fast = slow = pHead
for _ in range(k):
if not fast:
return None
fast = fast.next
while fast:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
这个的话先看看k值和链表是否为空是直接none,还有快指针在移动k格的时候是否为空是也是none,最后当快指针为null时候代表指针已经移动完成,接着输出慢指针链表就是要的答案
第九题 删除链表的倒数第n个节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @param n int整型
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self , head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
# write code here
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
fast = head
slow = dummy
for _ in range(n):
fast = fast.next
while fast:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
这个的话就是先定义一个新链表用于输出,慢指针是新链表,然后和找倒是节点一样的方案利用快指针然后使用慢指针的下一个节点接到下下个就等于删除了那个节点
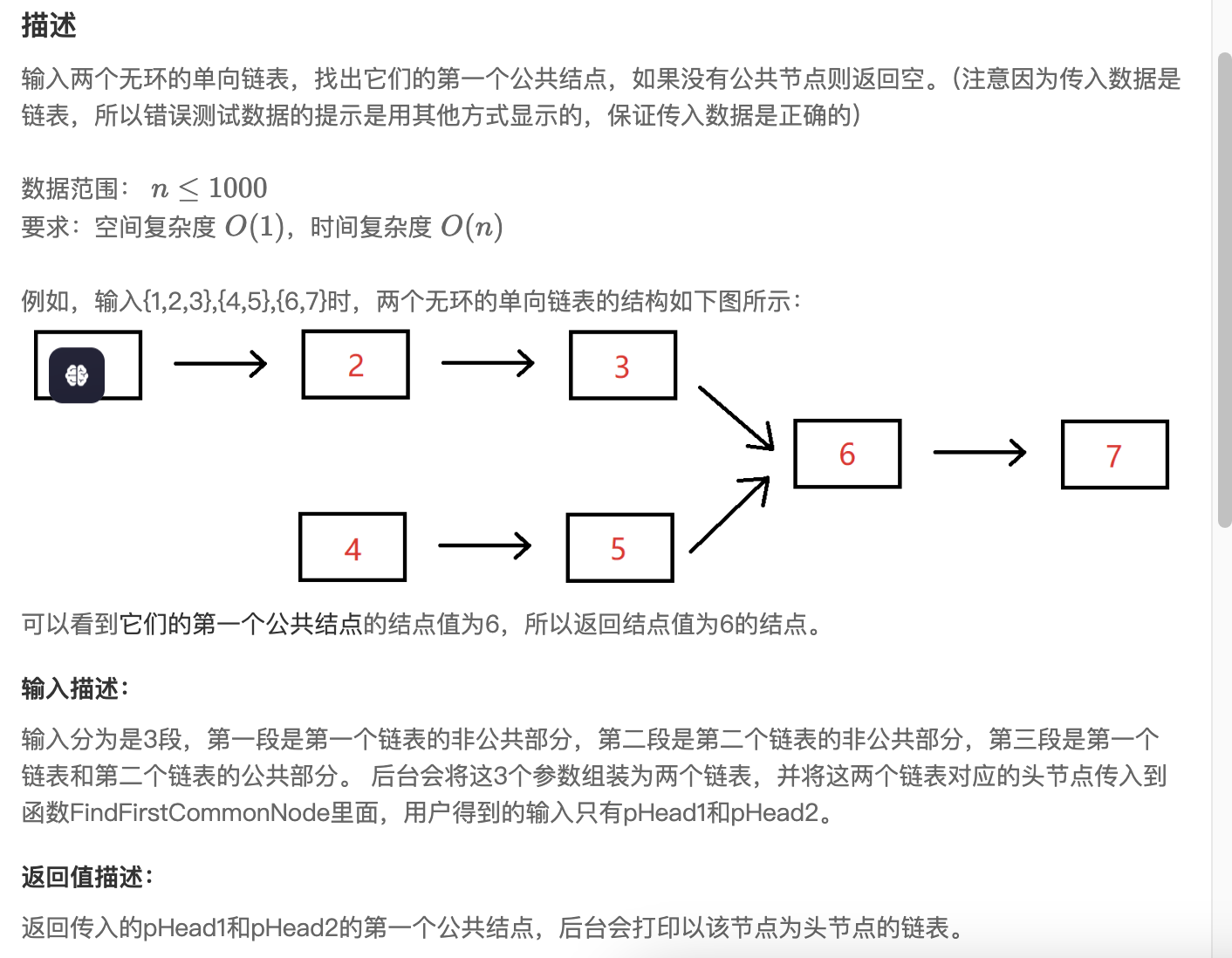
第十道 两个链表的第一个公共结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
import re
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
#
# @param pHead1 ListNode类
# @param pHead2 ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self , pHead1 , pHead2 ):
# write code here
if not pHead1 or not pHead2:
return None
p1 = pHead1
p2 = pHead2
while p1 != p2:
p1 = p1.next if p1 else pHead2
p2 = p2.next if p2 else pHead1
return p1
这个的话就是设计这两个指针是否相同,在移动的时候判断指针是不是为空是则变成另外一个链表
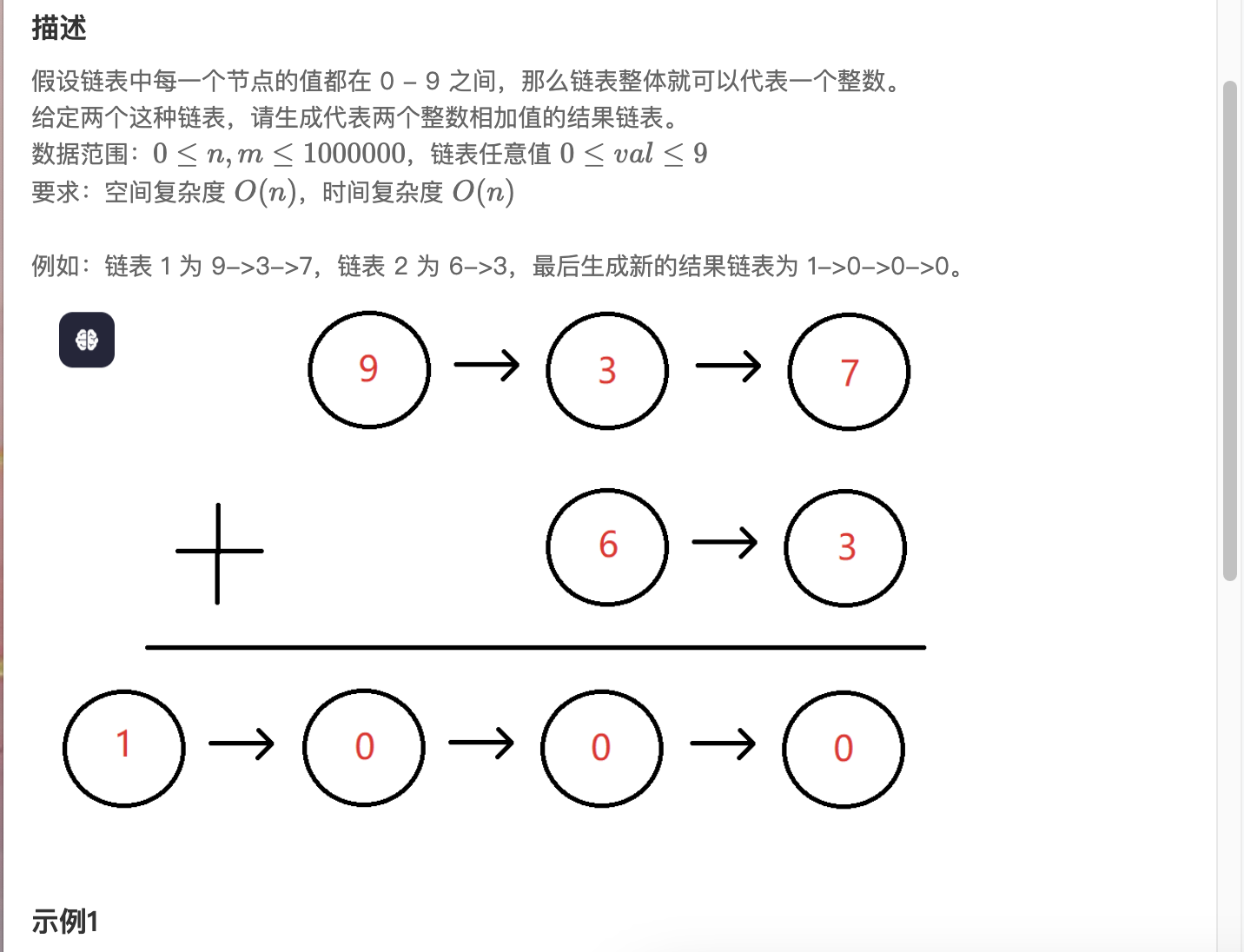
第十一道 链表相加(二)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head1 ListNode类
# @param head2 ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def addInList(self , head1: ListNode, head2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
stack1 = []
stack2 = []
while head1:
stack1.append(head1.val)
head1 = head1.next
while head2:
stack2.append(head2.val)
head2 = head2.next
carry = 0
result = None
while stack1 or stack2 or carry:
num1 = stack1.pop() if stack1 else 0
num2 = stack2.pop() if stack2 else 0
total = num1 + num2 + carry
carry = total // 10
digit = total % 10
new_node = ListNode(digit)
new_node.next = result
result = new_node
return result
先创建2个栈用于存储当前位值,循环把链表值压入栈,设置结果和进位值,循环当所有值都位NULL,carry取进位值,digit取余值,将余值已链表形式存储在新链表上不断把链表节点赋予result,最后输出
第十二道 单链表的排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类 the head node
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def sortInList(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
# 计算链表长度
length = 0
cur = head
while cur:
length += 1
cur = cur.next
# 创建哑节点作为链表头前驱
dummy_head = ListNode(0)
dummy_head.next = head
step = 1 # 初始步长
# 自底向上归并排序
while step < length:
pre = dummy_head # 已合并部分的尾节点
cur = dummy_head.next # 当前处理位置
while cur:
# 1. 分割第一段子链表
head1 = cur
head2 = self.split(head1, step)
# 2. 分割第二段子链表
next_head = None
if head2:
next_head = self.split(head2, step)
# 3. 合并两个子链表
merged_head, merged_tail = self.merge(head1, head2)
# 4. 连接已合并部分
pre.next = merged_head
pre = merged_tail # 更新尾节点
cur = next_head # 处理剩余链表
step *= 2 # 步长加倍
return dummy_head.next
def split(self, head, step):
"""分割链表:从head开始取step个节点,返回下段头节点"""
if not head:
return None
# 遍历到step位置
for _ in range(1, step):
if head.next:
head = head.next
else:
break
# 保存下一段头节点并断开链表
next_head = head.next
head.next = None
return next_head
def merge(self, l1, l2):
"""合并两个有序链表,返回头节点和尾节点"""
dummy_merge = ListNode(0) # 合并用哑节点
tail = dummy_merge
# 遍历两链表,按顺序合并
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
tail = tail.next
# 连接剩余部分
tail.next = l1 if l1 else l2
# 找到实际尾节点
while tail.next:
tail = tail.next
return dummy_merge.next, tail
这个我觉得很难因为它使用归并排序多了好多步骤,思想的话设计一个链表结合函数按照顺序排列,不过要注意链表的head和tail头节点和尾节点,还有一个断开头节点的函数用于划分节点的,最后就是自上而下合并
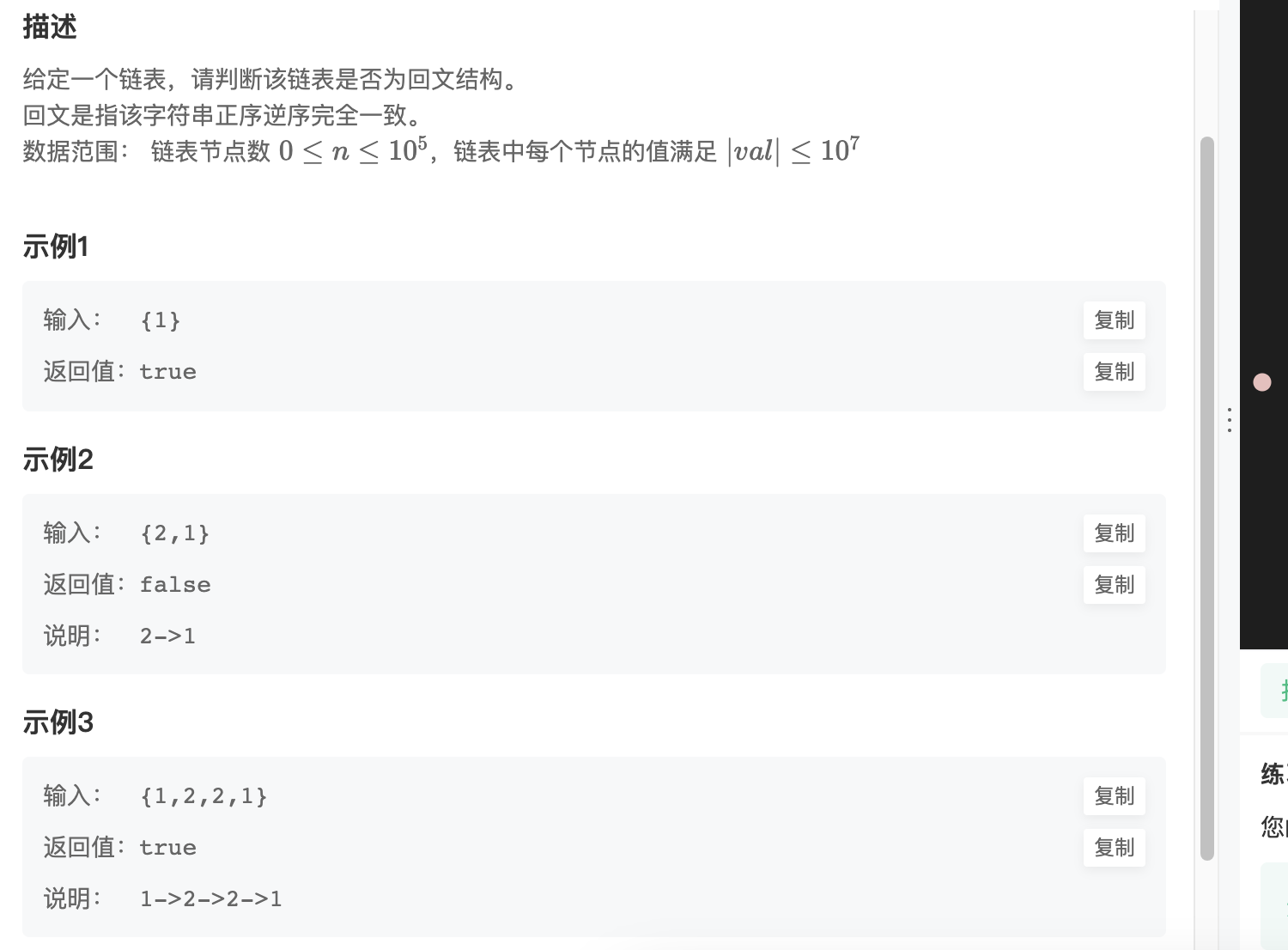
第十三道 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类 the head
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def isPail(self , head: ListNode) -> bool:
# write code here
if not head or not head.next:
return True
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
prev, curr = None, slow
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
reverse_head = prev
front, back = head, reverse_head
result = True
while back:
if back.val != front.val:
result = False
break
front = front.next
back = back.next
prev, curr = None, reverse_head
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = head
curr = next_node
slow.next = prev
return result
这道题是先判断是否为空如果为空或者1都是回文直接true,下面定义快慢指针反转链表根据反转链表和原链表进行判断正序和逆序读结果相同为回文,当快指针到达末尾时,慢指针位于中点(奇数为中间,偶数为中间偏右),最后把链表反转回来即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类 the head
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def isPail(self , head: ListNode) -> bool:
stack = []
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
stack.append(slow.val)
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast:
slow = slow.next
while slow:
if stack.pop() != slow.val:
return False
slow = slow.next
return True
不反转的方案更简单,先定义一个栈,进行快慢指针移动当快指针走完,慢指针刚好到中间位置,然后慢指针移动值存入栈,处理奇数的情况,然后判断栈是否等于慢指针移动的值相同的话直接移动不然终止返回false
第十四道 链表的奇偶重排
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
import re
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
if not head or not head.next:
return head
odd = head
even = head.next
evenhead = even
while even and even.next:
odd.next = even.next
odd = odd.next
even.next = odd.next
even = even.next
odd.next = evenhead
return head
从排的话就是3号位移动到2号位,5号位移动移动到4号位原被移动位踢掉然后把它加到从新拍好的奇链表
第十五道 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
curr = head
while curr and curr.next:
if curr.val == curr.next.val:
curr.next = curr.next.next
else:
curr = curr.next
return head
这个很简单循环链表如果下一个等于当前直接跳过不断操作即可
第十六道 删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param head ListNode类
# @return ListNode类
#
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# write code here
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
prev = dummy
curr = head
while curr and curr.next:
if curr.val == curr.next.val:
while curr.next and curr.val == curr.next.val:
curr = curr.next
prev.next = curr.next
else:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
return dummy.next
这个也挺简单 定义新链表,不断看当前值是否等于下个值是一直跳,并且最后前缀移动道没有重复的节点开始