niuke binary tree复盘
难度-Easy
niuke binary tree复盘
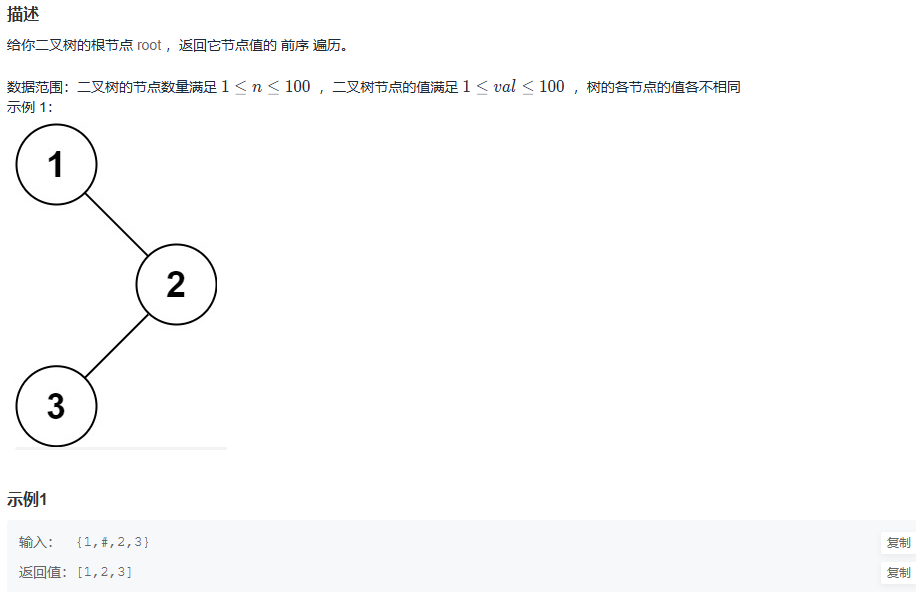
第一题 二叉树的前序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return int整型一维数组
#
class Solution:
def preorderTraversal(self , root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
# write code here
def dfs(node, result):
if not node: return
result.append(node.val)
dfs(node.left, result)
dfs(node.right, result)
res = []
dfs(root, res)
return res
写一个遍历函数用于循环遍历左右子树
第二题 二叉树的中序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return int整型一维数组
#
class Solution:
def inorderTraversal(self , root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
# write code here
def dfs(node, result):
if not node: return
dfs(node.left, result)
result.append(node.val)
dfs(node.right, result)
res = []
dfs(root, res)
return res
根前序差不多就是换一下位置
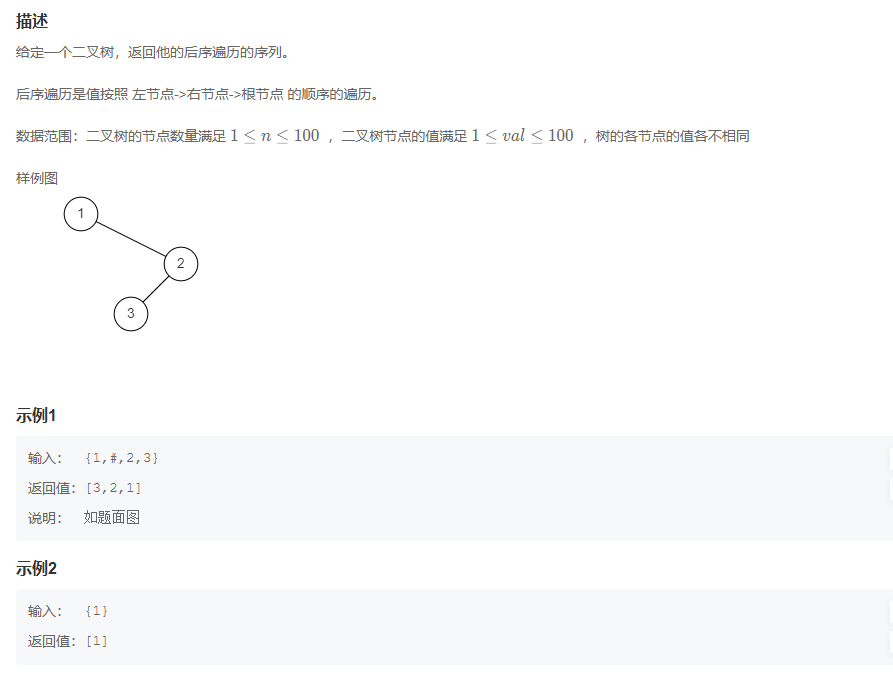
第三题 二叉树的后序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return int整型一维数组
#
class Solution:
def postorderTraversal(self , root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
# write code here
def dfs(node, result):
if not node: return
dfs(node.left, result)
dfs(node.right, result)
result.append(node.val)
res = []
dfs(root,res)
return res
没啥好说一招吃遍天
第四题 求二叉树的层序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
import queue
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return int整型二维数组
#
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self , root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
# write code here
if not root: return []
queue = deque([root])
result = []
while queue:
lever_size = len(queue)
lever_vals = []
for _ in range(lever_size):
node = queue.popleft()
lever_vals.append(node.val)
if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
result.append(lever_vals)
return result
这的话主要需要处理数的高,有了树高就好解决了,这里用了个包来处理数高
第五题 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pRoot TreeNode类
# @return int整型二维数组
#
class Solution:
def Print(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
# write code here
s, res = [], []
if not pRoot:
return res
s.append(pRoot)
num = 1
while s:
n = len(s)
temp = []
for i in range(n):
node = s.pop(0)
temp.append(node.val)
if node.left:
s.append(node.left)
if node.right:
s.append(node.right)
if num%2 != 0:
res.append(temp)
else:
res.append(temp[::-1])
num += 1
return res
这个的话首先定义一个输出队列,一个栈,先判断是否为空,然后把数加入到栈中,定义一个数字判断是否为奇数如果是从左到右加入,否则从右到左加入,循环临时的temp作为树打印,先进行队列,加入节点值,如果左右节点存在节点入栈
二叉树的最大深度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return int整型
#
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self , root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
ld = self.maxDepth(root.left)
rd = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(ld+1,rd+1)
这个最大深度就是直接自动查找匹配然后找最大即可
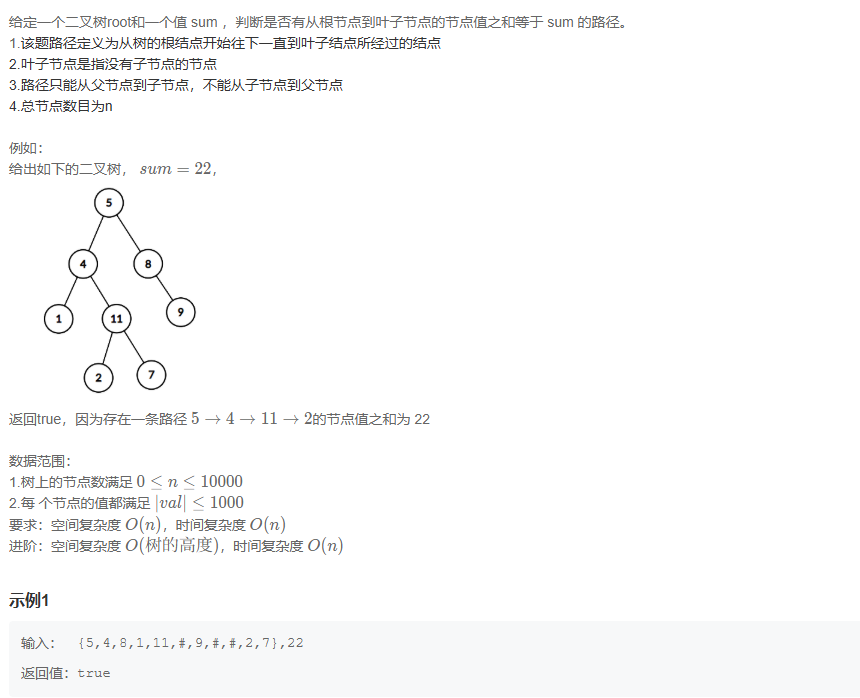
二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
import re
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @param sum int整型
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self , root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
# write code here
if not root: return False
sum -= root.val
if sum == 0 and not root.left and not root.right: return True
ld = self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum)
rd = self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum)
return ld or rd
这个和最大树差不多就是查左路径或者右路径是否满足不满足就false了
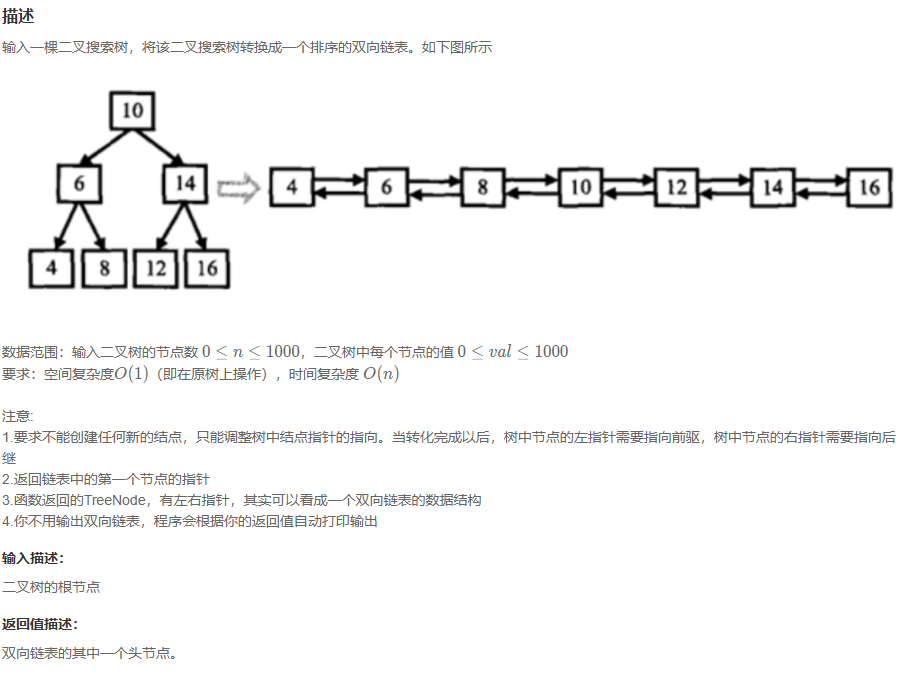
二叉搜索树与双向链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
#
# @param pRootOfTree TreeNode类
# @return TreeNode类
#
class Solution:
def Convert(self , pRootOfTree ):
# write code here
def func(root):
if not root: return None, None
left1, left2 = func(root.left)
right1, right2 = func(root.right)
root.left = left2
root.right = right1
return_left, return_right = root, root
if root.left:
left2.right = root
return_left = left1
if root.right:
right1.left = root
return_right = right2
return return_left, return_right
l,r = func(pRootOfTree)
return l
这个的话还是有点难度和绕的,先定义一个双向链表连接函数,return 返回2个值,定义链表左右的头和尾,初始化左的为尾,右为头,判断是否存在左右值,存在尾连接节点,返回值为头右相反这样函数调用实现双向链表
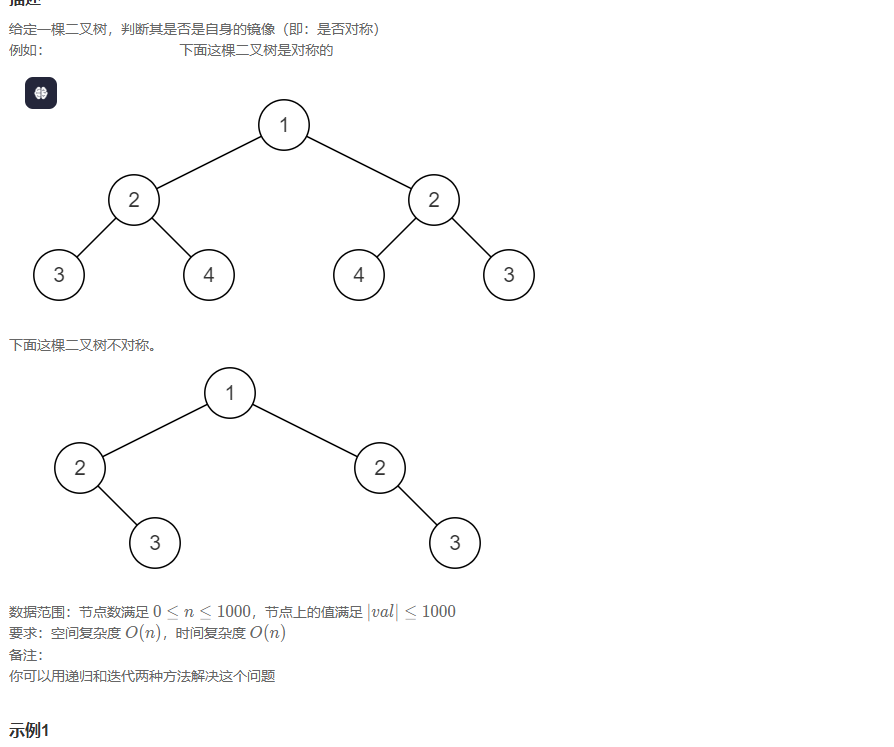
对称的二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
from re import L
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pRoot TreeNode类
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def isSymmetrical(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> bool:
# write code here
if not pRoot: return True
def isMirror(left, right):
if not left and not right:
return True
if not left or not right:
return False
if left.val != right.val:
return False
return isMirror(left.left, right.right) and isMirror(left.right, right.left)
return isMirror(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)
还是要定义函数去判断只需要保证left == right 其他false即可,不过要用递归操作。
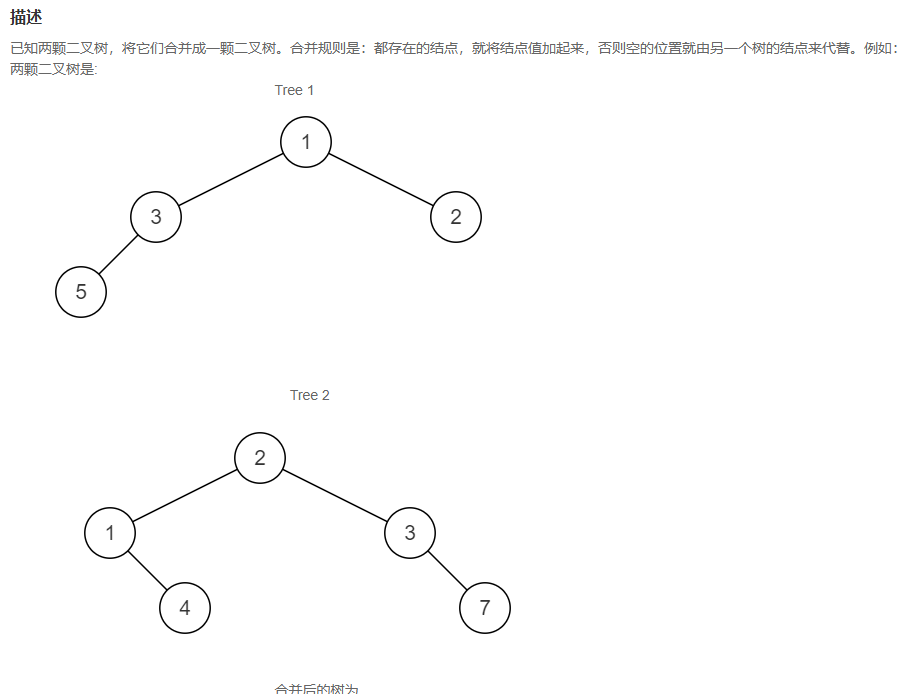
合并二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param t1 TreeNode类
# @param t2 TreeNode类
# @return TreeNode类
#
class Solution:
def mergeTrees(self , t1: TreeNode, t2: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
# write code here
if not t1:
return t2
if not t2:
return t1
head = TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val)
head.left, head.right = self.mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left), self.mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right)
return head
先判断是否2个数都在,头为值相加,返回头
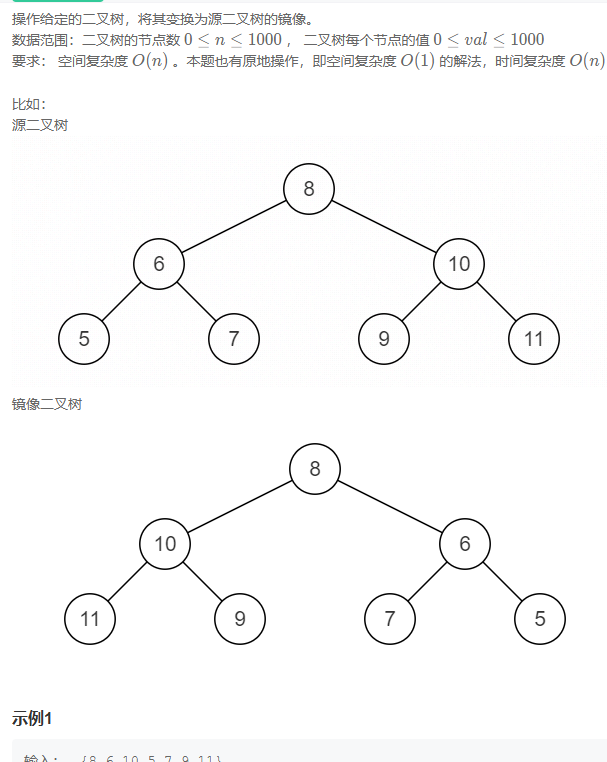
二叉树的镜像
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pRoot TreeNode类
# @return TreeNode类
#
class Solution:
def Mirror(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
# write code here
if not pRoot: return None
temp = pRoot.right
pRoot.right = pRoot.left
pRoot.left = temp
pRoot.left = self.Mirror(pRoot.left)
pRoot.right = self.Mirror(pRoot.right)
return pRoot
交换即可没有什么特殊的难度
判断是不是二叉搜索树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self , root: TreeNode) -> bool:
# write code here
res = self.inOrder(root)
if len(res) <= 1:
return True
for i in range(len(res) - 1):
if res[i] >= res[i+1]:
return False
return True
def inOrder(self, pRoot: TreeNode):
if not pRoot:return []
return self.inOrder(pRoot.left) + [pRoot.val] + self.inOrder(pRoot.right)
定义函数把树值存入到数组,然后判断左边值如果大于右边值则false其他情况为true
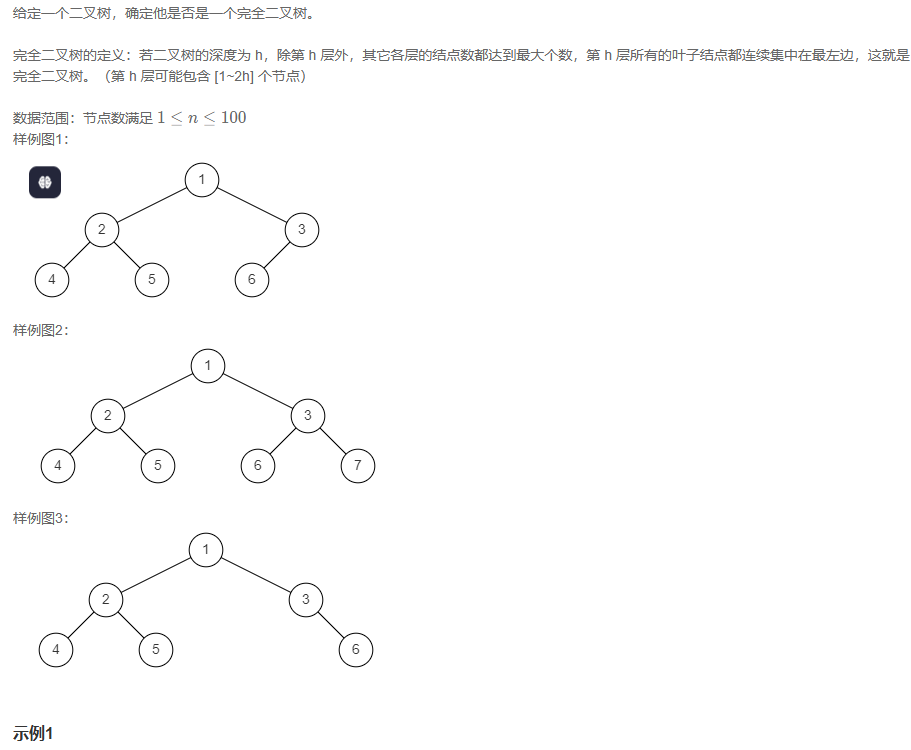
判断是不是完全二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def isCompleteTree(self , root: TreeNode) -> bool:
# write code here
if not root: return True
ret = [root]
while ret:
curr = ret.pop(0)
if curr:
ret.append(curr.left)
ret.append(curr.right)
else:
break
for i in ret:
if i:
return False
return True
用了队列的形式当然出现特殊字符则直接输出false,循环结束返回true
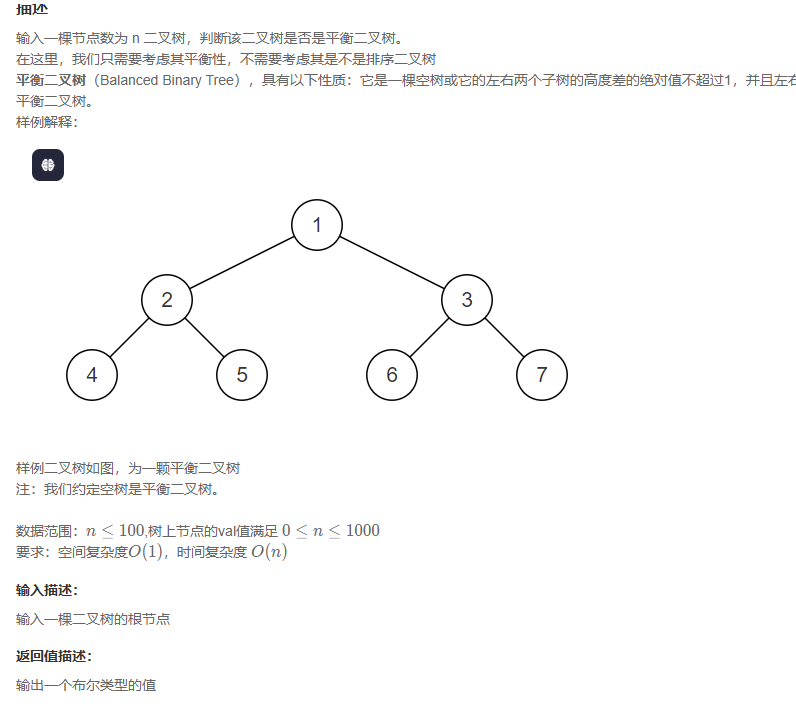
判断是不是平衡二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param pRoot TreeNode类
# @return bool布尔型
#
class Solution:
def IsBalanced_Solution(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> bool:
# write code here
if not pRoot: return True
if abs(self.TreeDepth(pRoot.left) - self.TreeDepth(pRoot.right)) < 2:
return self.IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot.left) and self.IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot.right)
else:
return False
def TreeDepth(self, rt):
return 1 + max(self.TreeDepth(rt.left), self.TreeDepth(rt.right)) if rt else 0
这个只需要判断树是否满足树是左右相减小于等于1
二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @param p int整型
# @param q int整型
# @return int整型
#
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self , root: TreeNode, p: int, q: int) -> int:
# write code here
if p < root.val and q < root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
elif p > root.val and q > root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
else:
return root.val
如果p和q小于当前节点说明节点在左节点上,p和q大于当前节点说明节点在右节点上,否则返回当前节点
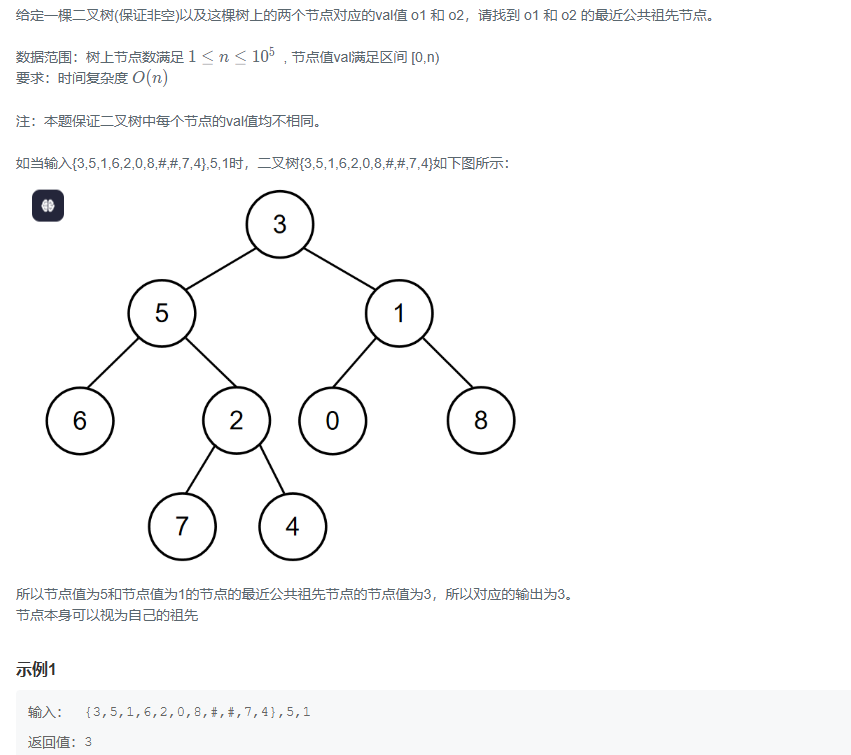
在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param root TreeNode类
# @param o1 int整型
# @param o2 int整型
# @return int整型
#
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self , root: TreeNode, o1: int, o2: int) -> int:
# write code here
if root == None:
return -1
if root.val == o1 or root.val ==o2:
return root.val
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, o1, o2)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, o1, o2)
if left != -1 and right == -1: return left
if right != -1 and left == -1: return right
if left == -1 and right == -1: return -1
return root.val
先判断是否为空,如果o1或者o2等于当前节点返回当前节点,判断左不为空,右为空返回左,右不为空,作为空返回右节点,都为空返回当前节点
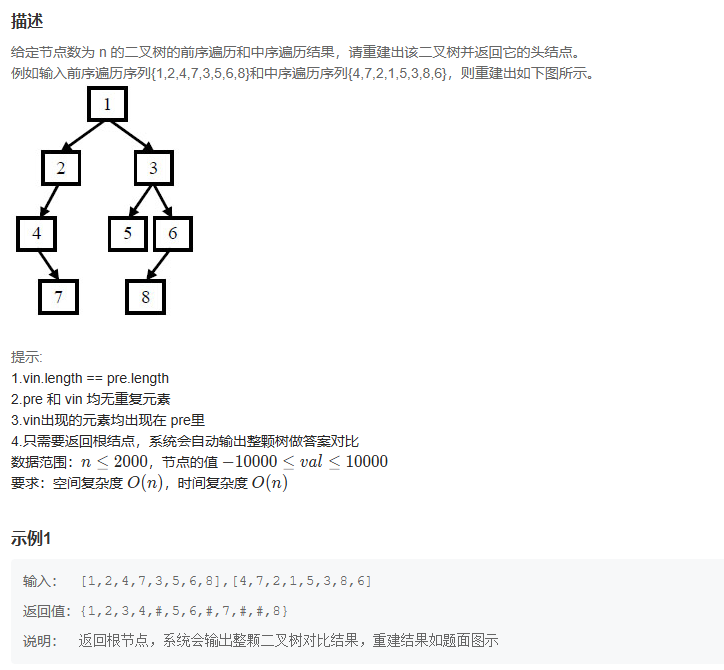
重建二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
#
# @param preOrder int整型一维数组
# @param vinOrder int整型一维数组
# @return TreeNode类
#
class Solution:
def reConstructBinaryTree(self , preOrder: List[int], vinOrder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
# write code here
if len(preOrder) == 0: return None
root = TreeNode(preOrder[0])
cur_root_index = vinOrder.index(preOrder[0])
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(preOrder[1:1+cur_root_index], vinOrder[0:cur_root_index])
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(preOrder[1+cur_root_index:],vinOrder[1+cur_root_index:])
return root
这个先判断前序是否为0如果为0直接返回None,然后找到切入点,通过切入点找左右节点位置
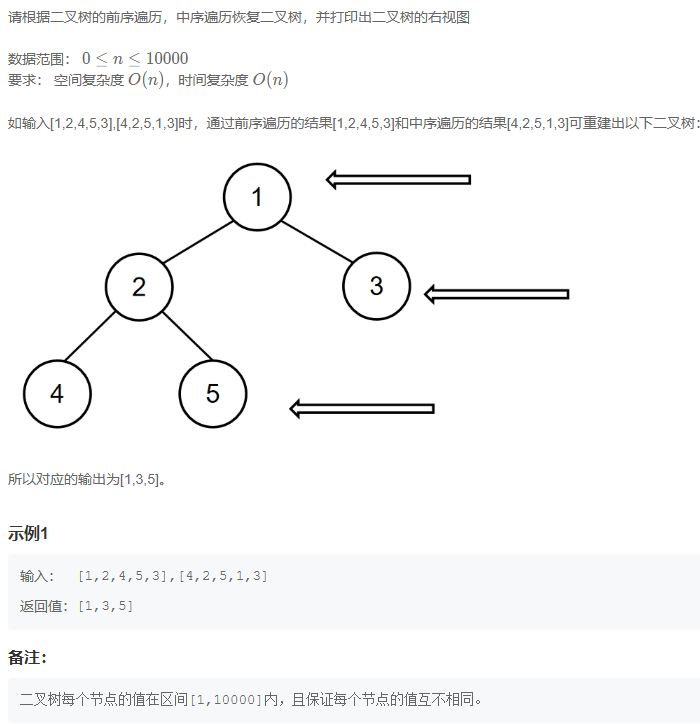
输出二叉树的右视图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
#
# 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
#
# 求二叉树的右视图
# @param preOrder int整型一维数组 先序遍历
# @param inOrder int整型一维数组 中序遍历
# @return int整型一维数组
#
class Solution:
def solve(self , preOrder: List[int], inOrder: List[int]) -> List[int]:
# write code here
if len(preOrder) == 0:return []
res = [preOrder[0]]
index = inOrder.index(preOrder[0])
left = self.solve(preOrder[1:index+1], inOrder[:index])
right = self.solve(preOrder[index+1:], inOrder[index+1:])
return res + right + left[len(right):]
跟重构差不多把树改数组即可,返回的话先返回右边最后返回左边
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.